Difference between pages "Premium Coffee Market Segmentation" and "Transactional memory in hardware"
From DolceraWiki
(Difference between pages)
Manikandan (Talk | contribs) (→Methodology) |
Manikandan (Talk | contribs) (→Contact Dolcera) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | == | + | ==Background== |
| + | ===Transactional memory=== | ||
| + | *Transactional memory is a general and flexible way to allow programs to read and modify disparate primary memory locations atomically as a single operation, much as a database transaction can atomically modify many records on disk. | ||
| + | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transactional_memory Transactional memory] attempts to simplify parallel programming by allowing a group of load and store instructions to execute in an atomic way. Transactional memory is a concurrency control mechanism analogous to database transactions for controlling access to shared memory in concurrent computing. A transaction is a piece of code that executes a series of reads and writes to shared memory. | ||
| + | *Transactional memory (TM) supports code sections that are executed atomically, i.e., so that they appear to be executed one at a time, with no interleaving between their steps. TM significantly reduces the difficulty of writing correct concurrent programs. A good TM implementation avoids synchronization between concurrently executed transactional sections unless they actually conflict. TM can significantly improve the performance and scalability of concurrent programs, as well as makes them easier to write, understand and maintain. | ||
| + | *[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220070156994%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20070156994&RS=DN/20070156994 Transactional memory] generally refers to a synchronization model that allows multiple threads to concurrently access a shared resource (such as a data structure stored in memory) without acquiring a lock as long as the accesses are non-conflicting, for example, as long as the accesses are directed to different portions of the shared resource. | ||
| + | '''[[More details]]''' | ||
| − | + | ---- | |
| − | + | ||
| − | == | + | ===Transactional programming models=== |
| − | + | *[http://research.sun.com/spotlight/2007/2007-08-13_transactional_memory.html Transactional programming models] can be supported in software using software-based transactional memory (STM), in hardware using hardware- based transactional memory (HTM), or in a combination of the two (Hybrid TM, or HyTM). | |
| + | **[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software_transactional_memory Software based Transactional memory] (STM) can allow sequences of concurrent operations to be combined into atomic transactions, thereby reducing the complexity of both programming and verification. STM is a scheme for concurrent programming with multiple threads that uses transactions similar to those used in databases. | ||
| + | **Hardware based Transactional memory (HTM) system requires no read or write barriers within the transaction code. The hardware manages data versions and tracks conflicts transparently. | ||
| + | **[http://www.eecs.harvard.edu/~fedorova/papers/asplos165-damron.pdf Hybrid Transactional memory] (HyTM) implements Transactional memory in software so that it can use best-effort Hardware Transactional memory (HTM) to boost performance but does not depend on HTM. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Software based Transactional memory=== | |
| + | *Software transactional memory (STM) is implemented in software. All speculative STM transactional data is stored in the system memory and indicated to be in a non-committed state. When the STM transaction commits, any data the transaction writes is indicated as committed and subsequently available to other threads and transactions. In certain STM systems, a flag may be set to indicate the data as committed and accessible and available in memory to other transactions. | ||
| − | + | ====DracoSTM==== | |
| + | *[http://eces.colorado.edu/~gottschl/dracoSTM/pubs/lcsd07-dracostm.pdf DracoSTM] is a high performance lock-based C++ Software Transactional memory research library. DracoSTM uses only native object-oriented language semantics, increasing its intuitiveness for developers while maintaining high programmability via automatic handling of composition, locks and transaction termination. | ||
| + | *DracoSTM is a lock-based STM system. At its core, DracoSTM uses one lock per thread to implement transactional reads and writes. This allows multiple transactions to simultaneously read and write without blocking other transactions’ progress. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ====Dynamic STM (DSTM)==== | |
| − | + | *[http://research.sun.com/scalable/pubs/PODC03.pdf Dynamic Software Transactional Memory (DSTM)] is a low-level application programming interface (API) for syn-chronizing shared data without using locks. | |
| − | + | *DSTM supports dynamic-sized data structures. DSTM has non-blocking implementation. The non-blocking property is obstruction-freedom. Dynamic means that the set of locations accessed by the transaction is not known in advance and is determined during its execution. | |
| − | + | *DSTM techniques allow transactions and transactional objects to be created dynamically.Transactions may determine the sequence of objects to access based on the values observed in objects accessed earlier in the same transaction. DSTM is well suited to the implementation of dynamic-sized data structures such as lists and trees. | |
| − | + | ====Dynamic Software Transactional Memory 2.0 (DSTM2)==== | |
| − | + | *[http://research.sun.com/scalable/pubs/OOPSLA2006.pdf DSTM2] is a Java-based software library that provides a flexible framework for implementing STM. DSTM2 significantly improves the programming interface of its predecessor DSTM. The code is provided in Java libraries and any Java programmer can use it easily. DSTM2 allows researchers to plug in their STM implementations and directly compare them with others. | |
| − | + | *The DSTM2 library assumes that multiple concurrent threads share data objects. The DSTM2 library provides a new kind of thread that can execute transactions, which access shared atomic objects. DSTM2 threads provide methods for creating new atomic classes and executing transactions. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ====Nonblocking Software Transactional Memory==== | |
| − | + | *[http://research.sun.com/scalable/pubs/PPoPP2008-NBSTM.pdf Nonblocking STMs] are obstruction free. Nonblocking Software Transactional Memory guarantees that, if a transaction is repeatedly retried and eventually encounters no interference from other transactions, then eventually the transaction commits successfully. | |
| − | + | *Nonblocking STM “steals” ownership of a memory location from another transaction, rather than waiting for the other transaction to explicitly release it. Accessing stolen locations is more complicated and expensive than accessing unstolen ones, but stealing is worthwhile in order to avoid waiting for another transaction that is delayed for a long time. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ====[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO2&Sect2=HITOFF&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsearch-bool.html&r=3&f=G&l=50&co1=AND&d=PTXT&s1=transactional.TI.&s2=memory.TI.&OS=TTL/transactional+AND+TTL/memory&RS=TTL/transactional+AND+TTL/memory Non-blocking conditions]==== | |
| + | =====Lock-free transactional memory===== | ||
| + | *'''Lock-free transactional memory:''' A transactional memory implementation is lock-free if all its operations are lock-free and if some thread repeatedly attempts to commit transactions, then eventually some thread performs a successful commit. | ||
| + | *'''Lock-freedom:''' An implementation of an operation is lock-free if after a finite number of steps of any execution of that operation, some operation execution completes (irrespective of the timing behavior of any concurrent operation executions). | ||
| − | + | =====Wait-free transactional memory===== | |
| + | *'''Wait-free transactional memory:''' A transactional memory implementation is wait-free if all its operations are wait-free and any thread that repeatedly attempts to commit transactions eventually performs a successful commit. | ||
| + | *'''Wait-freedom''': An implementation of an operation is wait-free if after a finite number of steps of any execution of that operation, that operation execution completes (irrespective of the timing behavior of any concurrent operation executions). | ||
| − | ''' | + | =====Obstruction-free transactional memory===== |
| + | *'''Obstruction-free transactional memory:''' A transactional memory implementation is obstruction-free if all its operations are obstruction-free and if some thread repeatedly attempts to commit transactions, and runs in isolation after some point, then it eventually performs a successful commit. | ||
| + | *'''Obstruction-freedom:''' An implementation of an operation is obstruction-free if every operation execution that executes in isolation after some point completes after a finite number of steps. | ||
| − | + | ===Hardware based Transactional memory=== | |
| − | + | *HTM comprises hardware transactions implemented entirely in processor hardware. For hardware transactions, data may be stored in hardware registers and cache, such that all cache actions are done atomically in hardware and data in the HTM is only written to the main memory upon committing the transaction. The HTM holds all the speculative writes without propagating to the main system memory, such as a Random Access Memory (RAM) device, until the transaction commits. If the hardware transaction aborts, then the cache lines holding the tentative writes in the HTM are discarded. HTM hardware transactions may utilize cache coherency protocols to detect and manage conflicts between HTM hardware transactions. The cache coherency protocols keep track of accesses within a hardware transaction. If two hardware transactions are accessing a same memory location, then the HTM aborts one transaction if there is a conflict, else the transaction's changes may be committed to the system memory. | |
| − | + | *HTM transactions usually require less overhead then STM transactions because HTM transactions occur entirely in hardware. HTM transactions may be limited to smaller transactions due to hardware limitations, whereas STM transactions can handle large and longer transactions. [http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220070143287%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20070143287&RS=DN/20070143287 Source] | |
| − | + | *The multi-core processor '''Rock''' supports [http://research.sun.com/scalable/pubs/TRANSACT2008-ATMTP-Apps.pdf Hardware Transactional Memory] (HTM). | |
| + | *'''Rock'''’s HTM feature is an important but modest first step in integrating HTM support into a mainstream commercial multi-core processor. | ||
| + | *'''Rock''' supports HTM with two new instructions, chkpt and commit, and a new checkpoint status (cps) register. A transaction is started by a chkpt instruction, and is terminated by either a commit instruction or the failure of the transaction. If a transaction fails, some indication of the cause of failure is stored in the cps register, and control is transferred to the PC-relative offset (fail pc) specified by the chkpt instruction. | ||
| − | + | ====Adaptive Transactional Memory Test Platform==== | |
| − | + | *The [http://www.cs.wisc.edu/gems/doc/gems-wiki/moin.cgi/ATMTP Adaptive Transactional Memory Test Platform] (ATMTP) provides a first-order approximation of the success and failure characteristics of transactions on '''Rock'''. ATMTP will allow developers to test and tune their code for '''Rock'''. | |
| − | + | *ATMTP correctly models '''Rock'''’s HTM-related instructions, and fairly accurately reflects most of the circumstances that cause '''Rock''' transactions to fail. ATMTP provides a good platform for experimenting with HTM-based code that will behave similarly on '''Rock'''. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ====Unbounded Hardware Transactional Memory (UHTM)==== | |
| − | + | *[http://supertech.csail.mit.edu/papers/xaction.pdf UHTM] is commited in-cache. When not possible, hardware “spills” transaction information into memory, allowing (essentially) unbounded transactions. UTM is more appealing for programmer, but is significantly more complicated. Unbounded means that there is no limit on the number of locations accessed by the transaction. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ====Best-effort Hardware Transactional Memory==== | |
| − | + | *Best-effort Hardware Transactional Memory transactions are committed in-cache and aborted if they don’t fit. Best-effort Hardware Transactional Memory has simple design.Best-effort Hardware Transactional Memory violates Principle of Least Astonishment. Programmer should not have to think about cache mapping, cache size, cache organization, etc. | |
| − | + | *[http://research.sun.com/scalable/pubs/TRANSACT2008-ATMTP-Apps.pdf Best-effort HTM] does not guarantee to support transactions of any size and duration, and thus is free to simply abort transactions that exceed on-chip resources for HTM or encounter difficult events or situations. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ====Split Hardware Transaction (SpHT)==== | |
| − | + | *The [http://research.sun.com/scalable/pubs/PPoPP2008-SpHT.pdf Split Hardware Transaction (SpHT])uses minimal software support to combine multiple segments of an atomic block, each executed using a separate hardware transaction, into one atomic operation. The idea of segmenting transactions can be used for many purposes, including nesting, local retry, or Else, and user-level thread scheduling. SpHT overcomes the limited expressive power of best-effort HTM while imposing overheads dramatically lower than STM and preserving useful guarantees such as strong atomicity provided by the underlying HTM. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ====Virtualized Transactional Memory (VTM)==== | |
| − | + | *[http://www.cs.wisc.edu/trans-memory/misc-papers/moir:hybrid-tm:tr:2005.pdf Virtualized TM (VTM)] maintains atomicity and isolation even if a transaction is interrupted by a cache overflow or a system event. VTM maps the key bookkeeping data structures for transactional execution (read set, write set, write buffer or undo-log) to virtual memory, which is effectively unbounded and is unaffected by system interruptions. The hardware caches hold the working set of these data structures. VTM also suggested the use of hardware signatures to avoid redundant searches through structures in virtual memory. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ====[http://research.microsoft.com/~larus/Papers/p80-larus.pdf Conflict detection]==== | |
| − | + | *HTM systems rely on a computer’s cache hierarchy and the cache coherence protocol to implement conflict detection. Caches observe all reads and writes issued by a processor, can buffer a significant amount of data, and can be searched efficiently because of their associative organization. All HTMs modify the first-level caches, but the approach extends to higher-level caches, both private and shared. | |
| − | + | *Conflict detection occurs as other processors receive the coherence messages from the committing transaction. Hardware looks up the received block address in the local caches. If the block is in a cache and has its R or W bit set, there is a read-write or a write-write conflict between the committing and the local transaction. The hardware signals a software handler, which aborts the local transaction and potentially retries it after a backoff period. | |
| − | + | *'''Direct memory updates:''' For direct updates, the hardware transparently logs the original value in a memory block before its first modification by a transaction. If the transaction aborts, the log is used to undo any memory updates. | |
| + | *'''Early conflict detection :''' For early conflict detection, the hardware acquires exclusive access to the cache block on the first write and maintains it until the transaction commits. | ||
| − | + | ===Hybrid Transactional memory (HyTM)=== | |
| − | + | *The HyTM approach is to provide an STM implementation that does not depend on hardware support beyond what is widely available today, and also to provide the ability to execute transactions using whatever HTM support is available in such a way that the two types of transactions can coexist correctly. | |
| − | + | *The key idea to achieving correct interaction between software transactions and hardware transactions is to augment hardware transactions with additional code that ensures that the transaction does not commit if it conflicts with an ongoing software transaction. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ====Phased Transactional Memory (PhTM)==== | |
| − | + | *[http://research.sun.com/scalable/pubs/TRANSACT2007-PhTM.pdf Phased Transactional Memory (PhTM])supports switching between different “phases”, each implemented by a different form of transactional memory support. PhTM allows to adapt between a variety of different transactional memory implementations. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ====Nonblocking Zero-Indirection Transactional Memory (NZTM)==== | |
| − | [http:// | + | *[http://research.sun.com/scalable/pubs/TRANSACT2007-NZTM.pdf Nonblocking Zero-Indirection Transactional Memory (NZTM)] is a nonblocking, zero-indirection object-based hybrid transactional memory system. NZTM can execute transactions using best-effort hardware transactional memory or by using compatible software transactional memory system. |
| − | == ''' | + | ====[http://research.microsoft.com/~larus/Papers/p80-larus.pdf Hardware-Accelerated STM (HASTM)]==== |
| + | *Hardware-Accelerated STM (HASTM) system proposes hardware support to reduce the overhead of STM instrumentation. The supplementary hardware allows software to build fast filters that could accelerate the common case of read set maintenance. | ||
| + | *HASTM provides the STM with two capabilities through per-thread mark bits at the granularity of cache blocks. | ||
| + | *'''Conflict detection:''' Software can check if a mark bit was previously set for a given block of memory and that no other thread wrote to the block since it was marked. | ||
| + | *'''Validation:''' Software can query if potentially there were writes by other threads to any of the memory blocks that the thread marked. | ||
| − | + | ====[http://research.microsoft.com/~larus/Papers/p80-larus.pdf Signature-Accelerated STM (SigTM)]==== | |
| + | *[http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1250673 Signature-Accelerated STM (SigTM)]uses hardware signatures to encode the read set and write set for software transactions. A hardware Bloom filter outside of the caches computes the signatures.b Software instrumentation provides the filters with the addresses of the objects read or written within a transaction. To detect conflicts, hardware in the computer monitors coherence traffic for requests for exclusive accesses to a cache block, which indicates a memory update. | ||
| + | *The hardware tests if the address in a request is potentially in a transaction’s read or write set by examining the transaction’s signatures. If so, the memory reference is a potential conflict and the STM can either abort a transaction or turn to software validation. | ||
| − | + | ---- | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ==Search strategy== | ||
| + | ===Search concepts=== | ||
| + | {|border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" width="100%" align="left" | ||
| + | |bgcolor = "#FFFF99"|'''Transactional memory''' | ||
| + | |bgcolor = "#FFFF99"|'''Atomic memory transactions''' | ||
| + | |bgcolor = "#FFFF99"|'''Concurrency control''' | ||
| + | |bgcolor = "#FFFF99"|'''Shared memory access''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |transactional memory |
| − | | | + | |atomic memory transactions |
| − | | | + | |concurrency control |
| − | + | |shared memory synchronization | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |transactional execution AND memory |
| − | | | + | |atomically memory accesses |
| − | | | + | |concurrent computing |
| − | + | |shared memory access | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |hybrid transactional memory |
| − | | | + | | |
| − | | | + | | |
| − | + | | | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |software transactional memory |
| − | | | + | | |
| − | | | + | | |
| − | + | | | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |hardware transactional memory |
| − | | | + | | |
| − | | | + | | |
| − | + | | | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |}<br clear="all"> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ---- | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Search strings=== | ||
| + | {|border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" width="100%" align="left" | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#FFFF99"|'''Concepts''' | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#FFFF99"|'''Scope''' | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#FFFF99"|'''Search string''' | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#FFFF99"|'''No of hits''' | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#FFFF99"|''' ''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#FFFF99"|'''Transactional memory''' |
| − | | | + | |rowspan = "3"|'''Search scope:''' US Granted US Applications EP-A EP-B WO JP DE-C,B DE-A DE-T DE-U GB-A FR-A; <br>'''Claims, Title or Abstract'''<br>'''Years: '''1836-2008 |
| − | |align = " | + | |(transactional ADJ memory) OR ((transactional ADJ execution) SAME memory) |
| − | + | |align = "center"|'''167''' | |
| + | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#FFFF99"|'''Other Keywords''' |
| − | | | + | |(atomic<nowiki>*</nowiki>4 NEAR2 memory NEAR2 (transaction<nowiki>*</nowiki>1 OR access<nowiki>*</nowiki>2)) OR (((concurrency ADJ control) OR (concurrent ADJ computing)) WITH ((shared ADJ memory) AND (synchronization OR access<nowiki>*</nowiki>2))) |
| − | |align = " | + | |align = "center"|'''24''' |
| − | + | | | |
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#FFFF99"|'''Final''' | ||
| + | |align = "center"|'''1 OR 2''' | ||
| + | |align = "center"|'''82 unique (189 patents including families)''' | ||
| + | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |}<br clear="all"> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ---- | |
| + | ==IP Trend== | ||
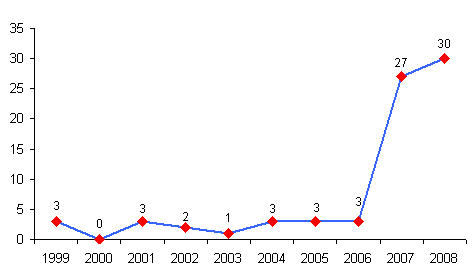
| + | *75 patents published in the last 10 years. | ||
| + | *Patent filing is more in the last 4 years(75 %) | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Year_wise_graph-Transactional_memory.jpg|align|thumb|center|500px|Year wise graph]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | |
| − | + | ---- | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==Key companies== | |
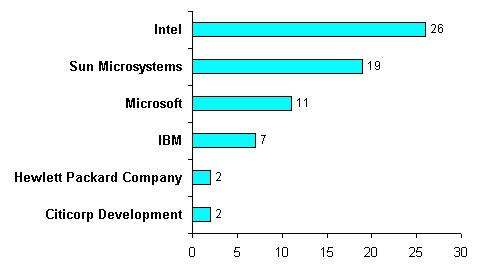
| + | * Intel(26 patents) and Sun Microsystems (19 patents) are major players. | ||
| + | * Microsoft(11 patents) and IBM(7 patents) are next to them. | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Assignee_graph-Transactional_memory.jpg|align|thumb|center|500px|Top Assignees]] | |
| − | + | ---- | |
| − | * | + | ==Top IPC and US Classes== |
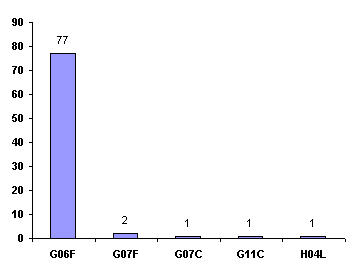
| + | *'''Top IPC class:''' G06F | ||
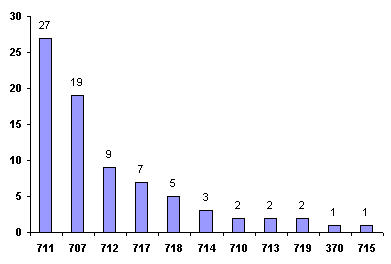
| + | *'''Top US class:''' 711, 707, 712, 717, 718 | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:IPC_class-Transactional_memory.jpg|align|thumb|left|500px|IPC class]] |
| + | [[Image:US_class-Transactional_memory.jpg|align|thumb|right|500px|US class]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ---- | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ==Sample analysis== | ||
{|border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" width="100%" | {|border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" width="100%" | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#969696"|<font color="#00FFFF">S.No.</font> |
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#969696"|<font color="#00FFFF">Patent/Publication No.</font> |
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#969696"|<font color="#00FFFF">Title</font> |
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#969696"|<font color="#00FFFF">Transactional memory</font> |
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#969696"|<font color="#00FFFF">Summary</font> |
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#969696"|<font color="#00FFFF">1</font> |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220040015642%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20040015642&RS=DN/20040015642 US20040015642A1]</u></font> |
| − | | | + | |Software transactional memory for dynamically sizable shared data structures |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|Dynamic STM (DSTM) |
| − | | | + | |A software transactional memory that allows concurrent non-blocking access to a dynamically sizable data structure defined in shared storage managed by the software transactional memory is described. The implementation is called dynamic software transactional memory (DSTM). DSTM techniques allow transactions and transactional objects to be created dynamically. The non-blocking property considered here is obstruction-freedom. |
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#969696"|<font color="#00FFFF">2</font> |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO2&Sect2=HITOFF&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsearch-adv.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&d=PG01&p=1&S1=20060085591.PGNR.&OS=DN/20060085591&RS=DN/20060085591 US20060085591A1]</u></font> |
| − | | | + | |Hybrid hardware and software implementation of transactional memory access |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|Phased Transactional Memory (PhTM) |
| − | | | + | |The invention relates to a hybrid hardware and software implementation of transactional memory accesses in a computer system. A processor including a transactional cache and a regular cache is utilized in a computer system that includes a policy manager to select one of a first mode (a hardware mode) or a second mode (a software mode) to implement transactional memory accesses. In the hardware mode the transactional cache is utilized to perform read and write memory operations and in the software mode the regular cache is utilized to perform read and write memory operations. |
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#969696"|<font color="#00FFFF">3</font> |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO2&Sect2=HITOFF&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsearch-adv.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&d=PG01&p=1&S1=20070028056.PGNR.&OS=DN/20070028056&RS=DN/20070028056 US20070028056A1]</u></font> |
| − | | | + | |Direct-update software transactional memory |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|Dynamic STM (DSTM) |
| − | | | + | |A transactional memory programming interface allows a thread to directly and safely access one or more shared memory locations within a transaction while maintaining control structures to manage memory accesses to those same locations by one or more other concurrent threads. Each memory location accessed by the thread is associated with an enlistment record, and each thread maintains a transaction log of its memory accesses. |
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#969696"|<font color="#00FFFF">4</font> |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO2&Sect2=HITOFF&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsearch-adv.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&d=PG01&p=1&S1=20070156780.PGNR.&OS=DN/20070156780&RS=DN/20070156780 US20070156780A1]</u></font> |
| − | | | + | |Protecting shared variables in a software transactional memory system |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|Dynamic STM (DSTM) |
| − | | | + | |For a variable accessed at least once in a software-based transactional memory system (STM) defined (STM-defined) critical region of a program, modifying an access to the variable that occurs outside any STM-defined critical region system by starting a hardware based transactional memory based transaction, within the hardware based transactional memory based transaction, checking if the variable is currently owned by a STM transaction, If the variable is not currently owned by a STM transaction, performing the access and then committing the hardware based transactional memory transaction and if the variable is currently owned by a STM transaction, performing a responsive action. |
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#969696"|<font color="#00FFFF">5</font> |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO2&Sect2=HITOFF&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsearch-adv.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&d=PG01&p=1&S1=20070156994.PGNR.&OS=DN/20070156994&RS=DN/20070156994 US20070156994A1]</u></font> |
| − | | | + | |Unbounded transactional memory systems |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|Unbounded Hardware Transactional Memory (UHTM) |
| − | | | + | |Methods and apparatus to provide unbounded transactional memory systems are described. Transactional memory is implemented through a table lookup mechanism. To access a shared resource, a thread may first check a table stored in memory to determine whether another thread is accessing the same portion of the shared resource. Accessing a table that is stored in memory may generate overhead that decreases performance. |
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#969696"|<font color="#00FFFF">6</font> |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO2&Sect2=HITOFF&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsearch-adv.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&d=PG01&p=1&S1=20070239942.PGNR.&OS=DN/20070239942&RS=DN/20070239942 US20070239942A1]</u></font> |
| − | | | + | |Transactional memory virtualization |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|Virtualized Transactional Memory (VTM) |
| − | | | + | |Methods and apparatus to provide transactional memory execution in a virtualized mode are described. Data corresponding to a transactional memory access request is stored in a portion of a memory after an operation corresponding to the transactional memory access request causes an overflow and a stored value may be updated for an occurrence of the overflow. |
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#969696"|<font color="#00FFFF">7</font> |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO2&Sect2=HITOFF&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsearch-adv.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&d=PG01&p=1&S1=20070300238.PGNR.&OS=DN/20070300238&RS=DN/20070300238 US20070300238A1]</u></font> |
| − | | | + | |Adapting software programs to operate in software transactional memory environments |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|Dynamic Software Transactional Memory 2.0 (DSTM2) |
| − | | | + | |Software transactional memory is used in non-managed language environments and with legacy codes without requiring a software programmer to change the programming paradigm they are currently used to. STM adapter system automatically transforms all the binary code executed within that block to execute atomically. STM adapter system automatically transforms lock-based critical sections in existing binary code to atomic blocks, |
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#969696"|<font color="#00FFFF">8</font> |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO2&Sect2=HITOFF&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsearch-adv.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&d=PG01&p=1&S1=20080005504.PGNR.&OS=DN/20080005504&RS=DN/20080005504 US20080005504A1]</u></font> |
| − | | | + | |Global overflow method for virtualized transactional memory |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|Virtualized Transactional Memory (VTM) |
| − | | | + | |A method and apparatus for virtualizing and/or extending transactional memory is described. Transactions are executed using local shared transactional memory, such as a cache memory. Upon overflowing the shared transactional memory, the transactional memory is virtualized and/or extended into a higher-level memory, such as a system memory. |
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#969696"|<font color="#00FFFF">9</font> |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO2&Sect2=HITOFF&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsearch-adv.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&d=PG01&p=1&S1=20080098374.PGNR.&OS=DN/20080098374&RS=DN/20080098374 US20080098374A1]</u></font> |
| − | | | + | |Method and apparatus for performing dynamic optimization for software transactional memory |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|Dynamic STM (DSTM) |
| − | | | + | |The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for performing dynamic optimization for STM. An optimistically immutable field is determined in the transaction to write. The transaction optimization unit keeps track of the status of object and class fields in a transaction. The transaction optimization unit invalidates methods corresponding to an optimistically immutable field in response to determining that the field has been written to and is therefore not immutable. |
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#969696"|<font color="#00FFFF">10</font> |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://www.wipo.int/pctdb/en/fetch.jsp?LANG=ENG&DBSELECT=PCT&SERVER_TYPE=19-10&SORT=41253138-KEY&TYPE_FIELD=256&IDB=0&IDOC=1629252&C=10&ELEMENT_SET=B&RESULT=1&TOTAL=1&START=1&DISP=25&FORM=SEP-0/HITNUM,B-ENG,DP,MC,AN,PA,ABSUM-ENG&SEARCH_IA=US2008050081&QUE WO2008088931A2]</u></font> |
| − | | | + | |FACILITATING EFFICIENT TRANSACTIONAL MEMORY AND ATOMIC OPERATIONS VIA CACHE LINE MARKING |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|Hardware-Accelerated STM (HASTM)-Conflict detection |
| − | | | + | |The system starts by executing a transaction for a thread, wherein executing the transaction involves placing load-marks on cache lines which are loaded during the transaction and placing store-marks on cache lines which are stored to during the transaction. Upon completing the transaction, the system releases the load-marks and the store-marks from the cache lines which were load-marked and store-marked during the transaction. Note that during the transaction, the load-marks and store-marks prevent interfering accesses from other threads to the cache lines. |
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |} |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ---- | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==Patent dashboard== | |
| − | + | '''[http://client.dolcera.com/dashboard/dashboard.html?workfile_id=388 Patent Categorization in Dashboard]''' | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==Contact Dolcera== | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | {| style="border:1px solid #AAA; background:#E9E9E9" align="center" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | ! style="background:lightgrey" | Samir Raiyani | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | '''Email''': [mailto:info@dolcera.com info@dolcera.com] |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | '''Phone''': +1-650-269-7952 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 00:22, 30 April 2009
Contents
- 1 Background
- 2 Search strategy
- 3 IP Trend
- 4 Key companies
- 5 Top IPC and US Classes
- 6 Sample analysis
- 7 Patent dashboard
- 8 Contact Dolcera
Background
Transactional memory
- Transactional memory is a general and flexible way to allow programs to read and modify disparate primary memory locations atomically as a single operation, much as a database transaction can atomically modify many records on disk.
- Transactional memory attempts to simplify parallel programming by allowing a group of load and store instructions to execute in an atomic way. Transactional memory is a concurrency control mechanism analogous to database transactions for controlling access to shared memory in concurrent computing. A transaction is a piece of code that executes a series of reads and writes to shared memory.
- Transactional memory (TM) supports code sections that are executed atomically, i.e., so that they appear to be executed one at a time, with no interleaving between their steps. TM significantly reduces the difficulty of writing correct concurrent programs. A good TM implementation avoids synchronization between concurrently executed transactional sections unless they actually conflict. TM can significantly improve the performance and scalability of concurrent programs, as well as makes them easier to write, understand and maintain.
- Transactional memory generally refers to a synchronization model that allows multiple threads to concurrently access a shared resource (such as a data structure stored in memory) without acquiring a lock as long as the accesses are non-conflicting, for example, as long as the accesses are directed to different portions of the shared resource.
Transactional programming models
- Transactional programming models can be supported in software using software-based transactional memory (STM), in hardware using hardware- based transactional memory (HTM), or in a combination of the two (Hybrid TM, or HyTM).
- Software based Transactional memory (STM) can allow sequences of concurrent operations to be combined into atomic transactions, thereby reducing the complexity of both programming and verification. STM is a scheme for concurrent programming with multiple threads that uses transactions similar to those used in databases.
- Hardware based Transactional memory (HTM) system requires no read or write barriers within the transaction code. The hardware manages data versions and tracks conflicts transparently.
- Hybrid Transactional memory (HyTM) implements Transactional memory in software so that it can use best-effort Hardware Transactional memory (HTM) to boost performance but does not depend on HTM.
Software based Transactional memory
- Software transactional memory (STM) is implemented in software. All speculative STM transactional data is stored in the system memory and indicated to be in a non-committed state. When the STM transaction commits, any data the transaction writes is indicated as committed and subsequently available to other threads and transactions. In certain STM systems, a flag may be set to indicate the data as committed and accessible and available in memory to other transactions.
DracoSTM
- DracoSTM is a high performance lock-based C++ Software Transactional memory research library. DracoSTM uses only native object-oriented language semantics, increasing its intuitiveness for developers while maintaining high programmability via automatic handling of composition, locks and transaction termination.
- DracoSTM is a lock-based STM system. At its core, DracoSTM uses one lock per thread to implement transactional reads and writes. This allows multiple transactions to simultaneously read and write without blocking other transactions’ progress.
Dynamic STM (DSTM)
- Dynamic Software Transactional Memory (DSTM) is a low-level application programming interface (API) for syn-chronizing shared data without using locks.
- DSTM supports dynamic-sized data structures. DSTM has non-blocking implementation. The non-blocking property is obstruction-freedom. Dynamic means that the set of locations accessed by the transaction is not known in advance and is determined during its execution.
- DSTM techniques allow transactions and transactional objects to be created dynamically.Transactions may determine the sequence of objects to access based on the values observed in objects accessed earlier in the same transaction. DSTM is well suited to the implementation of dynamic-sized data structures such as lists and trees.
Dynamic Software Transactional Memory 2.0 (DSTM2)
- DSTM2 is a Java-based software library that provides a flexible framework for implementing STM. DSTM2 significantly improves the programming interface of its predecessor DSTM. The code is provided in Java libraries and any Java programmer can use it easily. DSTM2 allows researchers to plug in their STM implementations and directly compare them with others.
- The DSTM2 library assumes that multiple concurrent threads share data objects. The DSTM2 library provides a new kind of thread that can execute transactions, which access shared atomic objects. DSTM2 threads provide methods for creating new atomic classes and executing transactions.
Nonblocking Software Transactional Memory
- Nonblocking STMs are obstruction free. Nonblocking Software Transactional Memory guarantees that, if a transaction is repeatedly retried and eventually encounters no interference from other transactions, then eventually the transaction commits successfully.
- Nonblocking STM “steals” ownership of a memory location from another transaction, rather than waiting for the other transaction to explicitly release it. Accessing stolen locations is more complicated and expensive than accessing unstolen ones, but stealing is worthwhile in order to avoid waiting for another transaction that is delayed for a long time.
Non-blocking conditions
Lock-free transactional memory
- Lock-free transactional memory: A transactional memory implementation is lock-free if all its operations are lock-free and if some thread repeatedly attempts to commit transactions, then eventually some thread performs a successful commit.
- Lock-freedom: An implementation of an operation is lock-free if after a finite number of steps of any execution of that operation, some operation execution completes (irrespective of the timing behavior of any concurrent operation executions).
Wait-free transactional memory
- Wait-free transactional memory: A transactional memory implementation is wait-free if all its operations are wait-free and any thread that repeatedly attempts to commit transactions eventually performs a successful commit.
- Wait-freedom: An implementation of an operation is wait-free if after a finite number of steps of any execution of that operation, that operation execution completes (irrespective of the timing behavior of any concurrent operation executions).
Obstruction-free transactional memory
- Obstruction-free transactional memory: A transactional memory implementation is obstruction-free if all its operations are obstruction-free and if some thread repeatedly attempts to commit transactions, and runs in isolation after some point, then it eventually performs a successful commit.
- Obstruction-freedom: An implementation of an operation is obstruction-free if every operation execution that executes in isolation after some point completes after a finite number of steps.
Hardware based Transactional memory
- HTM comprises hardware transactions implemented entirely in processor hardware. For hardware transactions, data may be stored in hardware registers and cache, such that all cache actions are done atomically in hardware and data in the HTM is only written to the main memory upon committing the transaction. The HTM holds all the speculative writes without propagating to the main system memory, such as a Random Access Memory (RAM) device, until the transaction commits. If the hardware transaction aborts, then the cache lines holding the tentative writes in the HTM are discarded. HTM hardware transactions may utilize cache coherency protocols to detect and manage conflicts between HTM hardware transactions. The cache coherency protocols keep track of accesses within a hardware transaction. If two hardware transactions are accessing a same memory location, then the HTM aborts one transaction if there is a conflict, else the transaction's changes may be committed to the system memory.
- HTM transactions usually require less overhead then STM transactions because HTM transactions occur entirely in hardware. HTM transactions may be limited to smaller transactions due to hardware limitations, whereas STM transactions can handle large and longer transactions. Source
- The multi-core processor Rock supports Hardware Transactional Memory (HTM).
- Rock’s HTM feature is an important but modest first step in integrating HTM support into a mainstream commercial multi-core processor.
- Rock supports HTM with two new instructions, chkpt and commit, and a new checkpoint status (cps) register. A transaction is started by a chkpt instruction, and is terminated by either a commit instruction or the failure of the transaction. If a transaction fails, some indication of the cause of failure is stored in the cps register, and control is transferred to the PC-relative offset (fail pc) specified by the chkpt instruction.
Adaptive Transactional Memory Test Platform
- The Adaptive Transactional Memory Test Platform (ATMTP) provides a first-order approximation of the success and failure characteristics of transactions on Rock. ATMTP will allow developers to test and tune their code for Rock.
- ATMTP correctly models Rock’s HTM-related instructions, and fairly accurately reflects most of the circumstances that cause Rock transactions to fail. ATMTP provides a good platform for experimenting with HTM-based code that will behave similarly on Rock.
Unbounded Hardware Transactional Memory (UHTM)
- UHTM is commited in-cache. When not possible, hardware “spills” transaction information into memory, allowing (essentially) unbounded transactions. UTM is more appealing for programmer, but is significantly more complicated. Unbounded means that there is no limit on the number of locations accessed by the transaction.
Best-effort Hardware Transactional Memory
- Best-effort Hardware Transactional Memory transactions are committed in-cache and aborted if they don’t fit. Best-effort Hardware Transactional Memory has simple design.Best-effort Hardware Transactional Memory violates Principle of Least Astonishment. Programmer should not have to think about cache mapping, cache size, cache organization, etc.
- Best-effort HTM does not guarantee to support transactions of any size and duration, and thus is free to simply abort transactions that exceed on-chip resources for HTM or encounter difficult events or situations.
Split Hardware Transaction (SpHT)
- The Split Hardware Transaction (SpHT)uses minimal software support to combine multiple segments of an atomic block, each executed using a separate hardware transaction, into one atomic operation. The idea of segmenting transactions can be used for many purposes, including nesting, local retry, or Else, and user-level thread scheduling. SpHT overcomes the limited expressive power of best-effort HTM while imposing overheads dramatically lower than STM and preserving useful guarantees such as strong atomicity provided by the underlying HTM.
Virtualized Transactional Memory (VTM)
- Virtualized TM (VTM) maintains atomicity and isolation even if a transaction is interrupted by a cache overflow or a system event. VTM maps the key bookkeeping data structures for transactional execution (read set, write set, write buffer or undo-log) to virtual memory, which is effectively unbounded and is unaffected by system interruptions. The hardware caches hold the working set of these data structures. VTM also suggested the use of hardware signatures to avoid redundant searches through structures in virtual memory.
Conflict detection
- HTM systems rely on a computer’s cache hierarchy and the cache coherence protocol to implement conflict detection. Caches observe all reads and writes issued by a processor, can buffer a significant amount of data, and can be searched efficiently because of their associative organization. All HTMs modify the first-level caches, but the approach extends to higher-level caches, both private and shared.
- Conflict detection occurs as other processors receive the coherence messages from the committing transaction. Hardware looks up the received block address in the local caches. If the block is in a cache and has its R or W bit set, there is a read-write or a write-write conflict between the committing and the local transaction. The hardware signals a software handler, which aborts the local transaction and potentially retries it after a backoff period.
- Direct memory updates: For direct updates, the hardware transparently logs the original value in a memory block before its first modification by a transaction. If the transaction aborts, the log is used to undo any memory updates.
- Early conflict detection : For early conflict detection, the hardware acquires exclusive access to the cache block on the first write and maintains it until the transaction commits.
Hybrid Transactional memory (HyTM)
- The HyTM approach is to provide an STM implementation that does not depend on hardware support beyond what is widely available today, and also to provide the ability to execute transactions using whatever HTM support is available in such a way that the two types of transactions can coexist correctly.
- The key idea to achieving correct interaction between software transactions and hardware transactions is to augment hardware transactions with additional code that ensures that the transaction does not commit if it conflicts with an ongoing software transaction.
Phased Transactional Memory (PhTM)
- Phased Transactional Memory (PhTM)supports switching between different “phases”, each implemented by a different form of transactional memory support. PhTM allows to adapt between a variety of different transactional memory implementations.
Nonblocking Zero-Indirection Transactional Memory (NZTM)
- Nonblocking Zero-Indirection Transactional Memory (NZTM) is a nonblocking, zero-indirection object-based hybrid transactional memory system. NZTM can execute transactions using best-effort hardware transactional memory or by using compatible software transactional memory system.
Hardware-Accelerated STM (HASTM)
- Hardware-Accelerated STM (HASTM) system proposes hardware support to reduce the overhead of STM instrumentation. The supplementary hardware allows software to build fast filters that could accelerate the common case of read set maintenance.
- HASTM provides the STM with two capabilities through per-thread mark bits at the granularity of cache blocks.
- Conflict detection: Software can check if a mark bit was previously set for a given block of memory and that no other thread wrote to the block since it was marked.
- Validation: Software can query if potentially there were writes by other threads to any of the memory blocks that the thread marked.
Signature-Accelerated STM (SigTM)
- Signature-Accelerated STM (SigTM)uses hardware signatures to encode the read set and write set for software transactions. A hardware Bloom filter outside of the caches computes the signatures.b Software instrumentation provides the filters with the addresses of the objects read or written within a transaction. To detect conflicts, hardware in the computer monitors coherence traffic for requests for exclusive accesses to a cache block, which indicates a memory update.
- The hardware tests if the address in a request is potentially in a transaction’s read or write set by examining the transaction’s signatures. If so, the memory reference is a potential conflict and the STM can either abort a transaction or turn to software validation.
Search strategy
Search concepts
| Transactional memory | Atomic memory transactions | Concurrency control | Shared memory access |
| transactional memory | atomic memory transactions | concurrency control | shared memory synchronization |
| transactional execution AND memory | atomically memory accesses | concurrent computing | shared memory access |
| hybrid transactional memory | |||
| software transactional memory | |||
| hardware transactional memory |
Search strings
| Concepts | Scope | Search string | No of hits | |
| Transactional memory | Search scope: US Granted US Applications EP-A EP-B WO JP DE-C,B DE-A DE-T DE-U GB-A FR-A; Claims, Title or Abstract Years: 1836-2008 |
(transactional ADJ memory) OR ((transactional ADJ execution) SAME memory) | 167 | |
| Other Keywords | (atomic*4 NEAR2 memory NEAR2 (transaction*1 OR access*2)) OR (((concurrency ADJ control) OR (concurrent ADJ computing)) WITH ((shared ADJ memory) AND (synchronization OR access*2))) | 24 | ||
| Final | 1 OR 2 | 82 unique (189 patents including families) |
IP Trend
- 75 patents published in the last 10 years.
- Patent filing is more in the last 4 years(75 %)
Key companies
- Intel(26 patents) and Sun Microsystems (19 patents) are major players.
- Microsoft(11 patents) and IBM(7 patents) are next to them.
Top IPC and US Classes
- Top IPC class: G06F
- Top US class: 711, 707, 712, 717, 718
Sample analysis
| S.No. | Patent/Publication No. | Title | Transactional memory | Summary |
| 1 | US20040015642A1 | Software transactional memory for dynamically sizable shared data structures | Dynamic STM (DSTM) | A software transactional memory that allows concurrent non-blocking access to a dynamically sizable data structure defined in shared storage managed by the software transactional memory is described. The implementation is called dynamic software transactional memory (DSTM). DSTM techniques allow transactions and transactional objects to be created dynamically. The non-blocking property considered here is obstruction-freedom. |
| 2 | US20060085591A1 | Hybrid hardware and software implementation of transactional memory access | Phased Transactional Memory (PhTM) | The invention relates to a hybrid hardware and software implementation of transactional memory accesses in a computer system. A processor including a transactional cache and a regular cache is utilized in a computer system that includes a policy manager to select one of a first mode (a hardware mode) or a second mode (a software mode) to implement transactional memory accesses. In the hardware mode the transactional cache is utilized to perform read and write memory operations and in the software mode the regular cache is utilized to perform read and write memory operations. |
| 3 | US20070028056A1 | Direct-update software transactional memory | Dynamic STM (DSTM) | A transactional memory programming interface allows a thread to directly and safely access one or more shared memory locations within a transaction while maintaining control structures to manage memory accesses to those same locations by one or more other concurrent threads. Each memory location accessed by the thread is associated with an enlistment record, and each thread maintains a transaction log of its memory accesses. |
| 4 | US20070156780A1 | Protecting shared variables in a software transactional memory system | Dynamic STM (DSTM) | For a variable accessed at least once in a software-based transactional memory system (STM) defined (STM-defined) critical region of a program, modifying an access to the variable that occurs outside any STM-defined critical region system by starting a hardware based transactional memory based transaction, within the hardware based transactional memory based transaction, checking if the variable is currently owned by a STM transaction, If the variable is not currently owned by a STM transaction, performing the access and then committing the hardware based transactional memory transaction and if the variable is currently owned by a STM transaction, performing a responsive action. |
| 5 | US20070156994A1 | Unbounded transactional memory systems | Unbounded Hardware Transactional Memory (UHTM) | Methods and apparatus to provide unbounded transactional memory systems are described. Transactional memory is implemented through a table lookup mechanism. To access a shared resource, a thread may first check a table stored in memory to determine whether another thread is accessing the same portion of the shared resource. Accessing a table that is stored in memory may generate overhead that decreases performance. |
| 6 | US20070239942A1 | Transactional memory virtualization | Virtualized Transactional Memory (VTM) | Methods and apparatus to provide transactional memory execution in a virtualized mode are described. Data corresponding to a transactional memory access request is stored in a portion of a memory after an operation corresponding to the transactional memory access request causes an overflow and a stored value may be updated for an occurrence of the overflow. |
| 7 | US20070300238A1 | Adapting software programs to operate in software transactional memory environments | Dynamic Software Transactional Memory 2.0 (DSTM2) | Software transactional memory is used in non-managed language environments and with legacy codes without requiring a software programmer to change the programming paradigm they are currently used to. STM adapter system automatically transforms all the binary code executed within that block to execute atomically. STM adapter system automatically transforms lock-based critical sections in existing binary code to atomic blocks, |
| 8 | US20080005504A1 | Global overflow method for virtualized transactional memory | Virtualized Transactional Memory (VTM) | A method and apparatus for virtualizing and/or extending transactional memory is described. Transactions are executed using local shared transactional memory, such as a cache memory. Upon overflowing the shared transactional memory, the transactional memory is virtualized and/or extended into a higher-level memory, such as a system memory. |
| 9 | US20080098374A1 | Method and apparatus for performing dynamic optimization for software transactional memory | Dynamic STM (DSTM) | The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for performing dynamic optimization for STM. An optimistically immutable field is determined in the transaction to write. The transaction optimization unit keeps track of the status of object and class fields in a transaction. The transaction optimization unit invalidates methods corresponding to an optimistically immutable field in response to determining that the field has been written to and is therefore not immutable. |
| 10 | WO2008088931A2 | FACILITATING EFFICIENT TRANSACTIONAL MEMORY AND ATOMIC OPERATIONS VIA CACHE LINE MARKING | Hardware-Accelerated STM (HASTM)-Conflict detection | The system starts by executing a transaction for a thread, wherein executing the transaction involves placing load-marks on cache lines which are loaded during the transaction and placing store-marks on cache lines which are stored to during the transaction. Upon completing the transaction, the system releases the load-marks and the store-marks from the cache lines which were load-marked and store-marked during the transaction. Note that during the transaction, the load-marks and store-marks prevent interfering accesses from other threads to the cache lines. |
Patent dashboard
Patent Categorization in Dashboard
Contact Dolcera
| Samir Raiyani |
|---|
| Email: info@dolcera.com |
| Phone: +1-650-269-7952 |