|
|
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | {{TOCrightEx}}
| + | =Overview= |
| − | == Rationale ==
| + | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) has recently emerged, in the field of medicinal chemistry, as one of the most attractive therapeutic targets for the development of selective inhibitors as promising new drugs for numerous serious pathologies, including Alzheimer's disease, stroke, bipolar disorders, chronic inflammatory processes, cancer, alopecia and Type II diabetes. The full potential of GSK-3 inhibitors is yet to be realised and the number of drug candidates being developed by both academic centres and pharmaceutical companies has increased exponentially in the last three years. This review discloses recent discoveries on peptides and small molecules targeting GSK-3. Antisense therapy for the modulation of GSK-3 expression is also discussed. Focusing attention on this exciting target could thus reap considerable clinical and economic rewards. [http://www.expertopin.com/doi/abs/10.1517/13543776.16.6.773 source] |
| − | * "Medication for men plagued by hair loss has become a topic of interest in Japan since a drug company began marketing it at the end of last year." March 5th, 2006 – [http://stophair.setupmyblog.com/?p=55]
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | * "An increasing number of companies are apparently turning the Chinese fear of a bald spot into big bucks with some doing so well they are branching out into other countries." February 16, 2006 – [http://stophair.setupmyblog.com/]
| |
| | | | |
| − | * "There is something in the air, or should we say in the hair, these days. Scientific research into hair loss remedies has never been more active or more exciting." June 7, 2006 - [http://www.prnewswire.com/cgi-bin/stories.pl?ACCT=109&STORY=/www/story/06-07-2005/0003821470&EDATE=]
| + | '''Protein name:'''Glycogen synthase kinase-3 alpha |
| | | | |
| − | == Alopecia IPMap ==
| + | '''Synonyms: '''EC 2.7.11.26; GSK-3 alpha |
| − | [http://www.dolcera.com/client/ds94x0s90akq9d7xb402fm/hairloss_map.htm Dolcera IPMap for Alopecia]
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | == Introduction ==
| + | '''Gene name :'''Name: GSK3A |
| | | | |
| − | === Hair Basics ===
| + | '''From :''' Homo sapiens (Human) [TaxID: 9606] |
| − | * Hair is a complex and delicate part of the body.
| + | |
| − | * Keeping it healthy and beautiful is a challenge.
| + | |
| − | * Hair grows everywhere on the body with the exception of the lips, eyelids, the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
| + | |
| − | * Hair is basically a form of skin.
| + | |
| − | * Hair is made up of a protein called keratin.
| + | |
| − | * Each shaft of hair is made of two or three inter-twined layers of keratin which grow from a follicle beneath the skin.
| + | |
| − | * Hair Structure - [http://www.pg.com/science/haircare/hair_twh_12.htm]
| + | |
| − | * Hair Cycle - [http://www.follicle.com/hair-structure-life-cycle.html]
| + | |
| − | [[Image:Hairbasics.jpg|thumb|center|500px|Structure of Hair root and Hair bulb]]
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | === What causes Hair loss? ===
| + | '''Function:''' Participates in the Wnt signaling pathway. Implicated in the hormonal control of several regulatory proteins including glycogen synthase, MYB and the transcription factor JUN. Phosphorylates JUN at sites proximal to its DNA-binding domain, thereby reducing its affinity for DNA. |
| − | * Decreased growth of the hair
| + | |
| − | * Increased shedding of the hair
| + | |
| − | * Breakage of hairs
| + | |
| − | * Conversion of thick terminal hairs to thin vellus hairs
| + | |
| − | [[Image:Facts.jpg|thumb|right|400px|Survey results from Japan]]
| + | |
| − | Both men and women lose hair for similar reasons. Hair loss in men is often more dramatic, and follows a specific pattern of loss, one of which has been termed '''“Male Pattern Baldness"''' or '''"Androgenetic Alopecia"'''.
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | === Androgenetic Alopecia === | + | ==Structural details == |
| − | * Gradual Onset.
| + | |
| − | * Transition from large, thick, pigmented terminal hairs to thinner, shorter, indeterminate hairs and finally to short, wispy, nonpigmented vellus hairs in the involved areas.
| + | |
| − | * Characterised by a receding hairline and/or hair loss on the top of the head.
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | '''Main Causes'''
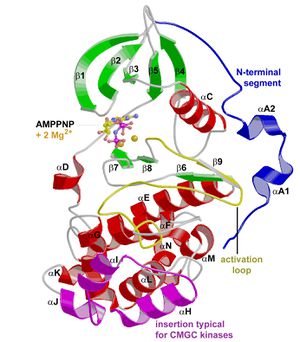
| + | * GSK3 has the typical two-domain kinase fold with a beta-strand domain (residues 25−138) at the N-terminal end and an alpha-helical domain at the C-terminal end (residues 139−343). <br> |
| − | * Genetic predisposition | + | * The ATP-binding site is at the interface of the alpha-helical and beta-strand domain and is bordered by the glycine-rich loop and the hinge. <br> |
| − | * Hormonal effect of androgen | + | * The activation loop (residues 200−226) runs along the surface of the substrate binding groove. <br> |
| − | * Reduction of blood circulation around hair follicle | + | * The C-terminal 39 residues (residues 344−382) are outside the core kinase fold and form a small domain that packs against the alpha-helical domain. <br>[[image:gsk3_2.jpg|right|300 px]] |
| − | * Deactivation of hair matrix cells | + | * The beta-strand domain consists of seven antiparallel beta-strands: strands 2−6 form a -barrel that is interrupted between strand 4 and 5 by a short helix (residue 96−102) that packs against the beta-barrel. <br> |
| | + | * This helix is conserved in all kinases, and two of its residues play key roles in the catalytic activity of the enzyme. Arg 96 is involved in the alignment of the two domains. Glu 97 is positioned in the active site and forms a salt bridge with Lys 85, a key residue in catalysis.<br> |
| | + | * Molecular weight: 46744.3 <br> |
| | + | * Theoretical pI: 8.98 <br> |
| | + | * Total number of negatively charged residues (Asp + Glu): 41 <br> |
| | + | * Total number of positively charged residues (Arg + Lys): 50 <br> |
| | | | |
| − | '''Some facts from Japan''' | + | '''Atomic composition:''' |
| | | | |
| − | * Market size: ¥ 30 Billion | + | ** Carbon C 2085 <br> |
| − | * Number of products: more than 100 | + | ** Hydrogen H 3285 <br> |
| | + | ** Nitrogen N 575 <br> |
| | + | ** Oxygen O 618 <br> |
| | + | ** Sulfur S 14 <br> |
| | + | * Formula: C2085H3285N575O618S14 |
| | + | * Total number of atoms: 6577 |
| | | | |
| − | (JICST-EPlus - Japanese Science & Technology)
| + | '''Prediction search done on NetPhos 2.0 server for GSK3''' |
| | | | |
| − | == Goals ==
| + | Prediction search done on NetPhos 2.0 server, which produces neural network predictions for serine, threonine and tyrosine phosphorylation sites in eukaryotic proteins. |
| | | | |
| − | The goal of this report is to:
| + | [[image:predication-gsk3.jpg|center|800 px]] |
| − | * Summarize IP activity over the years
| + | |
| − | * Identify major players
| + | |
| − | * Conduct patent analysis
| + | |
| − | a) Composition
| + | |
| − | b) Nature
| + | |
| − | c) Action
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | '''And then''' | + | '''DISPHOS (Disorder-Enhanced Phosphorylation Sites Predictor) Results''' |
| | | | |
| − | * Analyze patents pertaining to high sebum activity
| + | [[image:predication-gsk3-2.jpg|center|800 px]] |
| | | | |
| − | == Approach == | + | ==Amino Acid Sequence== |
| | | | |
| − | * A broad search was conducted on hair loss patents.
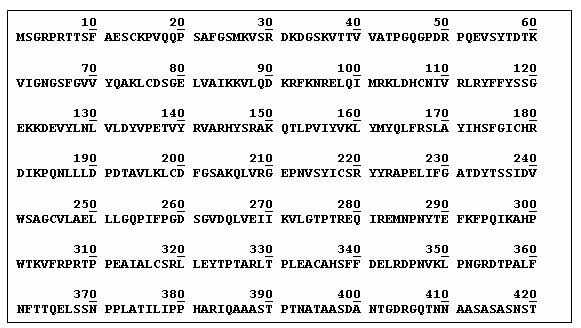
| + | GSK3B_HUMAN consists of 420 amino acids sequemnce. |
| − | * Patent information was sourced through SIP.
| + | |
| − | * A set of patents was selected for analysis.
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | Composition of treatment for causes are identified and categorized as follows:
| + | [[image:gsk-3 sequence.jpg|center|800 px]] |
| | | | |
| − | * Anti-androgen
| + | == Ways to inhibit GSK3== |
| − | * Minoxidil
| + | Possible ways in the art to inihibit GSK3 is illustrated in following figure: |
| − | * Double action (Anti-androgen + Mindoxidil)
| + | |
| − | * Hair matrix cells activator
| + | |
| − | * Sebum production inhibitor
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | == IP activity over years ==
| + | [[image:ways to inhibit gsk3.jpg|center|500 px]] |
| − | The graph indicates:
| + | |
| − | * Number of patents filed every 5 years (except for first 7 years).
| + | |
| − | * First solution proposed in 1973
| + | |
| − | * Filing trend indicates steep rise in activity recently.
| + | |
| − | [[Image:Year1.jpg|thumb|center|400px|IP Activity over years]] | + | |
| | | | |
| − | == Major Players == | + | =Beta-catenin= |
| − | [[Image:players.jpg|thumb|left|400px|Assignees with more than 20 patents ]]
| + | |
| − | [[Image:players1.jpg|thumb|center|400px|Assignees with fewer than 20 patents ]]<br>
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | * '''Active Assignees'''
| + | ==Structure== |
| − | Assignees currently active with more than 5 patents to their credit during 2000-2005.
| + | Beta-catenin consists of 781 amino acid residue. |
| − | * Warner with 9 patents,
| + | |
| − | * Bristol with 6 and
| + | |
| − | * Abbott with 5.
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | [[Image:Active.jpg|thumb|center|500px|Active Assignees]] | + | [[image:catenin.jpg|500 px|center]] |
| | | | |
| − | == Anti-androgens ==
| + | '''Amino Acid Sequence''' |
| − | * Anti-androgens are used in hormone therapy.
| + | |
| − | * Anti-androgens are designed to affect the hormones made in the adrenal glands. They don't stop the hormones from being made, but they stop them from having an effect leading to hair loss.
| + | |
| | | | |
| | + | 1 MATQADLMEL DMAMEPDRKA AVSHWQQQSY LDSGIHSGAT TTAPSLSGKG NPEEEDVDTS <br> |
| | + | 61 QVLYEWEQGF SQSFTQEQVA DIDGQYAMTR AQRVRAAMFP ETLDEGMQIP STQFDAAHPT<br> |
| | + | 121 NVQRLAEPSQ MLKHAVVNLI NYQDDAELAT RAIPELTKLL NDEDQVVVNK AAVMVHQLSK<br> |
| | + | 181 KEASRHAIMR SPQMVSAIVR TMQNTNDVET ARCTAGTLHN LSHHREGLLA IFKSGGIPAL<br> |
| | + | 241 VKMLGSPVDS VLFYAITTLH NLLLHQEGAK MAVRLAGGLQ KMVALLNKTN VKFLAITTDC<br> |
| | + | 301 LQILAYGNQE SKLIILASGG PQALVNIMRT YTYEKLLWTT SRVLKVLSVC SSNKPAIVEA<br> |
| | + | 361 GGMQALGLHL TDPSQRLVQN CLWTLRNLSD AATKQEGMEG LLGTLVQLLG SDDINVVTCA<br> |
| | + | 421 AGILSNLTCN NYKNKMMVCQ VGGIEALVRT VLRAGDREDI TEPAICALRH LTSRHQEAEM<br> |
| | + | 481 AQNAVRLHYG LPVVVKLLHP PSHWPLIKAT VGLIRNLALC PANHAPLREQ GAIPRLVQLL<br> |
| | + | 541 VRAHQDTQRR TSMGGTQQQF VEGVRMEEIV EGCTGALHIL ARDVHNRIVI RGLNTIPLFV<br> |
| | + | 601 QLLYSPIENI QRVAAGVLCE LAQDKEAAEA IEAEGATAPL TELLHSRNEG VATYAAAVLF<br> |
| | + | 661 RMSEDKPQDY KKRLSVELTS SLFRTEPMAW NETADLGLDI GAQGEPLGYR QDDPSYRSFH<br> |
| | + | 721 SGGYGQDALG MDPMMEHEMG GHHPGADYPV DGLPDLGHAQ DLMDGLPPGD SNQLAWFDTD<br> |
| | + | 781 l |
| | | | |
| − | '''What causes hair loss?'''
| + | ==Role of beta catenin== |
| − | * Testosterone is reduced to its active metabolite, Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by the enzyme 5 alpha reductase.
| + | |
| − | * DHT attaches to androgen receptor sites at the hair follicle.
| + | |
| − | * DHT causes gradual miniaturization of the follicle, which eventually results in hair loss.
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | '''How do anti-androgens treat hair loss?'''
| + | * Stabilized β-catenin can induce new hair follicles and trichofolliculoma-like tumors in skin. [http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=154144#B33 source] |
| − | * Anti-androgens compete with DHT to bind to the androgen receptor. | + | * Follicular (hair) and epidermal stem cells are located in the bulge region. |
| − | * Upon binding of anti-androgen in place of DHT, follicle miniaturization is lowered and hair loss prevented. | + | * In the absence of β-catenin, stem cells can differentiate into the epidermal lineage but not into the hair follicular lineage. [http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=154144 source] |
| | + | * In a research, expression of stabilized β-catenin in the epidermis of transgenic mice resulted in hair follicle morphogenesis. [http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2121/7/4#B8 source] |
| | | | |
| − | === Functions of Anti-androgen ===
| |
| − | [http://www.revivogen.com/revivogen/work.html Anti-androgen]
| |
| | | | |
| − | [[Image:Andogen1.jpg|thumb|center|500px|Functions of Anti-androgen]]
| |
| | | | |
| − | === IP Map for Anti-androgen ===
| + | [[image:in action.jpg|center|400 px]] |
| − | | + | |
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="8", style="#008080"
| + | |
| − | !width="30" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Pat/Pub#'''
| + | |
| − | !width="30" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Nature'''
| + | |
| − | !width="100" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Composition'''
| + | |
| − | !width="100" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Composition action'''
| + | |
| − | |- style="height:20px"
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220060009430%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20060009430&RS=DN/20060009430 US20060009430]
| + | |
| − | BLOTECH (2004)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Natural extracts
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Palmetto berry extract (fatty acids & sterols), Pumpkin seed extract (Vitamins-B, alpha-linolenic acid, amino acids and phytosterols), Quercetin (Flavonoids) and Beta-sitosterol (Rice bran, wheat germ, corn oils and soybeans)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Fatty acids – Inhibit testosterone
| + | |
| − | Sterols - Mechanism of action unknown.
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | Quercetin results in cell growth cycle.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | Beta-sitosterol reduce inflammation on scalp
| + | |
| − | |- style="height:20px"
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220060009427%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20060009427&RS=DN/20060009427 US20060009427]
| + | |
| − | WARNER LAMBERT(2004)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Organic compound
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|New class of 4-cycloalkoxy benzonitrile derivatives and salts
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Acts as androgen receptor modulators and blocks formation of DHT.
| + | |
| − | |- style="height:20px"
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050085467%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050085467&RS=DN/20050085467 US20050085467]
| + | |
| − | WARNER LAMBERT(2004)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Organic compound
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|New class of 6-sulfonamido-quinolin-2-one and 6-sulfonamido-2-oxo-chromene derivatives.
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|The compounds inhibit, or decrease, activation of androgen receptor by androgens.
| + | |
| − | |- style="height:20px"
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050118282%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050118282&RS=DN/20050118282 US20050118282]
| + | |
| − | APHIOS Corp (2003)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Natural extracts
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Supercritical fluid isolate of Saw Palmetto and Sperol (Serenoa repens berry) and their analogs or derivatives.
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Modulates androgenic activity by inhibiting 5.alpha.-reductase activity.
| + | |
| − | |- style="height:20px"
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220060009429%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20060009429&RS=DN/20060009429 US20060009429]
| + | |
| − | Fundacion Pablo Cassara (2003)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Nucleotide
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Pharmacologically active oligonucleotides (encompass both DNA and S-DNA bond)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Oligonucleotides inhibit androgen receptor (AR) expression at very low concentrations in skin and hair follicle
| + | |
| − | |- style="height:20px"
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220030007941%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20030007941&RS=DN/20030007941 US20030007941]
| + | |
| − | PFIZER INC (2001)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Organic compound
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Thyromimetic compounds (structurally similar to thyronine) with finasteride, or cyproterone acetate
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Activates thyroid hormone receptors in hair follicle which in turn promote elasticisation of follicle walls and hair follicle
| + | |
| − | |- style="height:20px"
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220030073616%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20030073616&RS=DN/20030073616 US20030073616]
| + | |
| − | N/A (1995)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Peptides/nucleic acid
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Bradykinin antagonist (peptide of plasma origin from kininogen precursor-kallikrein)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Inhibit synthesis of bradykinin receptors or compounds by binding to B2 receptor
| + | |
| − | |- style="height:20px"
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://v3.espacenet.com/textdoc?DB=EPODOC&IDX=EP0279010&F=0 EP0279010]
| + | |
| − | KAO Corp (1987)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Natural extracts
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Walnut extract (leaves/pericarps) with an organic solvent
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Blocks formation of DHT
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Minoxidil ==
| + | |
| − | * Minoxidil is a "potassium channel opener" that leads to vasodilation.
| + | |
| − | * The drug is available in two forms. Oral minoxidil is used to treat high blood pressure and the topical solution form is used to treat hair loss and baldness.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''What causes hair loss?'''
| + | |
| − | * A thick network of tiny veins and arteries lines the outer wall of the follicle. Blood pumps through the bulb and hair via this network.
| + | |
| − | * DHT accumulates in the hair follicles and roots, constricting the blood supply of oxygen and nutrients to the hair roots; which is also seen to possibly contribute towards hair loss.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''How does Minoxidal treat hair loss?'''
| + | |
| − | * Minoxidal is applied to the scalp topically, where it dilates blood vessels in the scalp and sustains the hair follicles for longer period of time.
| + | |
| − | * Scientists and researchers are not exactly sure of how Minoxidil leads to this effect.
| + | |
| − | * Minoxidil sulfate (MS) appears to be the active metabolite responsible for hair growth stimulation.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Functions of Monoxidil === [http://www.nurseminerva.co.uk/diagrams.htm#Diagram%201 Minoxidil]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | [[Image:minoxidil1.jpg|thumb|center|500px|Functions of Monoxidil]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === IP Map for Minoxidil ===
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="2"
| + | |
| − | !width="100" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Pat/Pub#'''
| + | |
| − | !width="75" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Nature'''
| + | |
| − | !width="300" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Composition'''
| + | |
| − | !width="300" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Composition action'''
| + | |
| − | |- style="height:100px"
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220040157856%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20040157856&RS=DN/20040157856 US20040157856]
| + | |
| − | WARNER LAMBERT(2002)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Organic compound
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Benzopyran compounds
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Rapidly metabolizes, and causes reduced cardiovascular effects as compared to other known potassium channel openers
| + | |
| − | |- style="height:100px"
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050053572%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050053572&RS=DN/20050053572 US20050053572]
| + | |
| − | LG HOUSEHOLD & HEALTH CARE(2001)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Natural extracts
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Sophora flavescens extract (alkaloids & flavonoids, luteolin-7-glucose and cytosine) Hinokitiol (Taiwan hinoki oil, Aomori, Western Red Cedar oil) and Nicotinamide (Vitamin B complex)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Promotes function of cell activity and dilates blood vessels
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Double action (Anti-androgen + Minoxidil) ==
| + | |
| − | * Combination of Minoxidil + Anti-androgen (double action) composition for effective treatment of Male-Pattern Baldness.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''What is the problem with using only Anti-androgen therapy?'''
| + | |
| − | * Anti-androgen is not effective in addressing the issue of vasocontriction around hair follicles due to sebum oil build up.
| + | |
| − | * Anti-androgen only prevent binding of DHT to androgen receptors. However, the effects of improper oxygen and nutrient supply to the brain due to vasocontriction still remains and gradually causes hair loss.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''What is the problem with using only Minoxidal therapy?'''
| + | |
| − | * Minoxidil-based products are generally not effective in stopping hair loss as minoxidil does not block the harmful effects of DHT in the scalp and hair follicles.
| + | |
| − | * Minoxidil simply dilates blood vessels in the scalp. However, the harmful DHT is still being produced in the body and still getting into the scalp and hair follicles and causing eventual hair loss.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''How is the combination of Anti-androgens and Minoxidil effective?'''
| + | |
| − | * Anti-androgens target the problem of DHT binding to androgen receptors and prevents follicle miniaturization.
| + | |
| − | * Minoxidil causes vasodilation and therefore improves supply of oxygen and nutrients to the hair follicle and roots.
| + | |
| − | * Combination therapy therefore proves to be much more effective than individual therapy.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Functions of (Anti-androgen + Minoxidil) === [http://www.revivogen.com/revivogen/work.html Anti-androgen ]and [http://www.xandrox.net/articles/article01.htm Minoxidil]
| + | |
| − | [[Image:Doubleaction1.jpg|thumb|center|500px|Functions of (Anti-androgen + Minoxidil)]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === IP Map for (Anti-androgen + Minoxidil) ===
| + | |
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="3"
| + | |
| − | !width="100" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Pat/Pub#'''
| + | |
| − | !width="75" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Nature'''
| + | |
| − | !width="300" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Composition'''
| + | |
| − | !width="300" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Composition action'''
| + | |
| − | |- style="height:100px"
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220060052405%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20060052405&RS=DN/20060052405 US20060052405]
| + | |
| − | N/A(2000)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Peptides
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Testosterone blocker or vascular toner (Flutamide, cyproterone acetate, spironolactone, progesterone, or analogs or derivatives) and minoxidil mixed along with non-retinoid penetration enhance and sunscreen
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Inhibits 5.alpha.-reductase activity (block DHT) and increase blood flow on the scalp
| + | |
| − | |- style="height:100px"
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050123577%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050123577&RS=DN/20050123577 US20050123577]
| + | |
| − | L'OREAL(2000)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Peptides
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Prostaglandin (polyunsaturated fatty acids) EP-2, EP-3 EP-4 receptor agonist with Minoxidil, 2,4-diaminopyrimidine 3-oxide, and Aminexil, cyclic AMP
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Minoxidil (designed to mimic nitric oxide's effects) grows hair via prostaglandin-H synthase stimulation. EP-3 and EP-4 are expressed in anagen hair follicles which induce a reduction in the level of cAMP
| + | |
| − | |- style="height:100px"
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=6447762.PN.&OS=PN/6447762&RS=PN/6447762 US6447762]
| + | |
| − | COLOMER GROUP(1999)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Natural extract
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Hop extract (oil contains terpenes and humulene), Rosemary extract (hydroalcohol), Swertia extract (glycol with a swertiamarin), Silanodiol salicylate (biologically active silicon compound)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Inhibits activity of 5-alpha-reductase, protects follicular cell membranes by neutralizing action of oxidation reaction in tissues, stimulates hair follicles and blood circulation to the hair root, supplies oxygen and nutrients to base of follicle, retains humidity, avoids dehydration of scalp
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Hair matrix cell activator ==
| + | |
| − | Hair matrix cell activator is a substance that acts at the matrix cells in the hair follicle preventing their degradation.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''What causes hair loss?'''
| + | |
| − | * Stem cells are interspersed within the basal layer of the outer root sheath and in an area called the bulge.
| + | |
| − | * Stem cells migrate to hair matrix where they start to divide and differentiate, under the influence of substances produced by cells of the dermal papilla.
| + | |
| − | * Perifollicular matrix cells undergo slow degradation which prevents follicle stimulation.
| + | |
| − | * Hair follicle activation is required for hair growth and thus inhibition of follicle activation eventually leads to hair loss.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''How does hair cell matrix activator treat hair loss?'''
| + | |
| − | * Hair cell matrix activator slows down and inhibits degradation of the perifollicular matrix.
| + | |
| − | * This leads to an increase in hair follicle matrix cells that differentiate from progenitor stem cells.
| + | |
| − | * Matrix activator allows activation of hair matrix cells and therefore follicle stimulation leading to hair growth.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Functions of Hair matrix cell activator === [http://www.ijdb.ehu.es/fullaccess/fulltext.04023/ft163.pdf Hair matrix cell activator]
| + | |
| − | [[Image:Hair matrix.jpg|thumb|center|500px|Functions of Hair matrix cell activator ]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === IP Map for Hair matrix cell activator ===
| + | |
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="2"
| + | |
| − | !width="100" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Pat/Pub#'''
| + | |
| − | !width="75" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Nature'''
| + | |
| − | !width="300" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Composition'''
| + | |
| − | !width="300" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Composition action'''
| + | |
| − | |- style="height:100px"
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220020052498%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20020052498&RS=DN/20020052498 US20020052498]
| + | |
| − | SHISEIDO(1999)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Organic compound
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|(2-substituted oxyphenyl) alkanamide derivative and its salt
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Mechanism of action has not been made clear, having excellent hair follicle activating action and regrowth promoting effect
| + | |
| − | |- style="height:100px"
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220040071647%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20040071647&RS=DN/20040071647 US20040071647]
| + | |
| − | L'OREAL(1998)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Peptides
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Metalloprotease (MMP-9) inhibitor (thiol or a hydroxamate) other than chelating calcium ions
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Reducing the expression of MMPs (Metalloproteases) in the scalp - slow down or inhibit the degradation of the perifollicular matrix (extracellular matrix surround the hair follicle)
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Sebum Production Inhibitor ==
| + | |
| − | Sebum Production Inhibitor is a substance that prevents the synthesis of sebum, mixture of lipid substances.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''What causes hair loss?'''
| + | |
| − | * Sebum is a fatty acid substance secreted from sebaceous glands associated with hair follicles.
| + | |
| − | * Hair can get heavy sebum build-up and mixes with cholesterol to form a hardened plug around the bottom part of the hair bulb.
| + | |
| − | * Hardened plugs prevent cell respirations and eventually lead to hair loss.
| + | |
| − | * Bacteria will also attach to the hardened plug and this can also cause further cause problems with hair growth.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''How does Sebum production inhibitor treat hair loss?'''
| + | |
| − | * The inhibitor prevents synthesis of sebum and slows down accumulation and mixing of sebum with cholesterol leading to hardened plugs.
| + | |
| − | * Reduction of sebum results in unclogged hair follicles/bulbs and allows oxygen and nutrients from reaching the hair follicle.
| + | |
| − | * Reduction in sebum also prevents vasoconstriction.
| + | |
| − | * Sum result of these effects of Sebum production inhibitor is prevention of hair loss.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | * The inhibitor blocks the excessive sebum production produces greasy effect on hair and scalp and also responsible for thinning and loosing of hair.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Functions of Sebum Production Inhibitor ===
| + | |
| − | [[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:HairFollicle.jpg Sebum Production Inhibitor]]
| + | |
| − | [[Image:Sebum1.jpg|thumb|center|500px|Functions of Sebum Production Inhibitor]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === IPMap for Sebum Production Inhibitor ===
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="3", style="#008080"
| + | |
| − | !width="100" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Pat/Pub#'''
| + | |
| − | !width="75" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Nature'''
| + | |
| − | !width="300" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Composition'''
| + | |
| − | !width="300" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Composition action'''
| + | |
| − | |- style="height:100px"
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050277699%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050277699&RS=DN/20050277699 US20050277699]
| + | |
| − | Unilever(2005)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Natural extract and organic compound
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Polyamine (putrescine, spermine or spermidine) analogs and/or derivatives; DFMO; N-acetyl cysteines; neutralized salts of a non-hydroxy C2-C40 dicarboxylic acids, preferably malonate salts; and mixtures thereof.
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Decreasing sebum production and/or pore size
| + | |
| − | |- style="height:100px"
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050244362%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050244362&RS=DN/20050244362 US20050244362]
| + | |
| − | KAO COPR.(2004)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Natural extract and organic compound
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Avocado oil (Butyl esters of fatty acids)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Reduce sebum of the hair and scalp
| + | |
| − | |- style="height:100px"
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=4529587.PN.&OS=PN/4529587&RS=PN/4529587 US4529587]
| + | |
| − | Unilever(1982)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|organic compound
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan |Biotin antagonist or a salt thereof
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Decrease activity of the enzyme acetyl-SCoA-carboxylase and hence reduce lipid synthesis in sebaceous glands so that less sebum is produced
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Composition nature matrix ==
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === IPMap: Composition nature matrix ===
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="11", style="#008080"
| + | |
| − | !width="50" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Year'''
| + | |
| − | !width="75" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Organic Compound'''
| + | |
| − | !width="75" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Natural extracts'''
| + | |
| − | !width="75" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Peptides'''
| + | |
| − | !width="75" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Nucleotides'''
| + | |
| − | !width="75" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Natural extract + Organic comp'''
| + | |
| − | |- style="height:10px"
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|2005
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|UNILEVER (1)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|2004
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|WARNER (1)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|BLOTECH (1)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|KAO (1)
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|2003
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|WARNER (1)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|APHIOS (1)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|FUNDIACION (1)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|2002
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|WARNER (1)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|2001
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan |PFIZER (1)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|LG HEALTH-CARE (1)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|2000
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|L’OREAL (1) / N/A (1)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|1999
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|SHISEDIO (1)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|COLOMER (1)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|1998
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|L’OREAL (1)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|1995
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|N/A (1)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|1987
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|KAO (1)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|1982
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|UNILEVER (1)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|....
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Focus of patents ==
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="17", style="#008080"
| + | |
| − | !width="600" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Focus of patents'''
| + | |
| − | !width="20" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Patent no.'''
| + | |
| − | !width="20" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Rec. no.'''
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|2-substituted oxyphenyl alkanamide derivative having excellent hair growth effect.
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220020052498%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20020052498&RS=DN/20020052498 US20020052498]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|1
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Thyromimetic compounds, and its role in treating hair loss
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220030007941%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20030007941&RS=DN/20030007941 US20030007941]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|2
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Saw Palmetto berry extract, pumpkin seed extract, sitosterol and quercetin for the treatment and prevention of the biologically detrimental effects of DHT
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220060009430%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20060009430&RS=DN/20060009430 US20060009430]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|3
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|4-cycloalkoxy benzonitriles and its use as androgen receptor modulators
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220060009427%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20060009427&RS=DN/20060009427 US20060009427]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|4
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Supercritical fluid isolate of Saw Palmetto, Sperol for inhibition of 5-.alpha.-reductase activity
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050118282%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050118282&RS=DN/20050118282 US20050118282]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|5
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|New class of quinolin-2-ones and chromen-2-ones andtheir use as androgen receptor antagonists
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050085467%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050085467&RS=DN/20050085467 US20050085467]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|6
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Antiandrogen oligonucleotides usable for the treatment of dermatological androgen-related disorders
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220060009429%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20060009429&RS=DN/20060009429 US20060009429]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|7
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Bradykinin antagonists for stimulating or inducing hair growth and/or arresting hair loss
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220030073616%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20030073616&RS=DN/20030073616 US20030073616]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|8
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Extract from walnut leaves and/or pericarps as 5 alpha -reductase inhibitor
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://v3.espacenet.com/textdoc?DB=EPODOC&IDX=EP0279010&F=0 EP0279010]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|9
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Stimulating hair growth using benzopyrans
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220040157856%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20040157856&RS=DN/20040157856 US20040157856]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|10
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Sophora flavescens extract, Coicis semen extract, clove extract, etc for promoting hair growth, function of cell activity and dilating peripheral blood vessels.
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050053572%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050053572&RS=DN/20050053572 US20050053572]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|11
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Compositions to prevent or reduce hair loss
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220060052405%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20060052405&RS=DN/20060052405 US20060052405]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|12
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Prostaglandin EP-3 receptor antagonists for reducing hair loss
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050123577%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050123577&RS=DN/20050123577 US20050123577]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|13
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Synergic effect arising from the interaction of active ingredients, consisting of three plant extracts and a synthetic organosilicic compound for prevent hair loss and stimulate hair growth
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=6447762.PN.&OS=PN/6447762&RS=PN/6447762 US6447762]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|14
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Metalloprotease inhibitors to induce and/or stimulate the growth
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220040071647%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20040071647&RS=DN/20040071647 US20040071647]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|15
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Method of decreasing sebum production and pore size
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050277699%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050277699&RS=DN/20050277699 US20050277699 ]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|16
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Method for reducing sebum on the hair and skin
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=4529587.PN.&OS=PN/4529587&RS=PN/4529587 US4529587]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|17
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Focus of patents by technology ===
| + | |
| − | [[Image:Technologyfocus2.jpg|thumb|center|700px|Technology focus]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Distribution of patents ==
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | === By patent types ===
| + | |
| − | [[Image:Didtribution.jpg|thumb|center|700px|Distribution based on patent types ]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === By key ingredients ===
| + | |
| − | [[Image:key1.jpg|thumb|center|700px|Distribution of key ingredients]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === By target disease ===
| + | |
| − | [[Image:target.jpg|thumb|center|700px|Distribution based on target diseases]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Key ingredients vs. Target disease ===
| + | |
| − | [[Image:key&target1.jpg|thumb|center|1000px|Key ingredients vs. Target disease]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Target species ===
| + | |
| − | [[Image:Species.jpg|thumb|center|700px|Target species]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Mode of administration ===
| + | |
| − | [[Image:Mode.jpg|thumb|center|700px|Mode of administration]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Product type vs. Product form ===
| + | |
| − | [[Image:prod.jpg|thumb|center|700px|Product type vs. Product form]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Distribution based on different aspects ==
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === List of patents ===
| + | |
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="9", style="#008080"
| + | |
| − | !width="20" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Rec. no.'''
| + | |
| − | !width="70" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Patent no.'''
| + | |
| − | !width="20" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Rec. no.'''
| + | |
| − | !width="70" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Patent no.'''
| + | |
| − | |- style="height:10px"
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|1
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220020052498%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20020052498&RS=DN/20020052498 US20020052498]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|10
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220040157856%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20040157856&RS=DN/20040157856 US20040157856]
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|2
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220030007941%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20030007941&RS=DN/20030007941 US20030007941]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|11
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050053572%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050053572&RS=DN/20050053572 US20050053572]
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|3
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220060009430%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20060009430&RS=DN/20060009430 US20060009430]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|12
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220060052405%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20060052405&RS=DN/20060052405 US20060052405]
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|4
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220060009427%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20060009427&RS=DN/20060009427 US20060009427]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|13
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050123577%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050123577&RS=DN/20050123577 US20050123577]
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|5
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050118282%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050118282&RS=DN/20050118282 US20050118282]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|14
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=6447762.PN.&OS=PN/6447762&RS=PN/6447762 US6447762]
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|6
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050085467%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050085467&RS=DN/20050085467 US20050085467]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|15
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220040071647%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20040071647&RS=DN/20040071647 US20040071647]
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|7
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220060009429%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20060009429&RS=DN/20060009429 US20060009429]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|16
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050277699%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050277699&RS=DN/20050277699 US20050277699]
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|8
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220030073616%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20030073616&RS=DN/20030073616 US20030073616]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|17
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050244362%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050244362&RS=DN/20050244362 US20050244362]
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|9
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://v3.espacenet.com/textdoc?DB=EPODOC&IDX=EP0279010&F=0 EP0279010]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|18
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=4529587.PN.&OS=PN/4529587&RS=PN/4529587 US4529587]
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Patents by target diseases ===
| + | |
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="16", style="#008080"
| + | |
| − | !width="600" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Target disease/ disorder'''
| + | |
| − | !width="20" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Patent no.'''
| + | |
| − | !width="20" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Rec. no.'''
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Alopecia areata, alopecia pityrodes or alopecia seborrheica, or androgenic alopecia (i.e. male pattern baldness)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220020052498%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20020052498&RS=DN/20020052498 US20020052498]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|1
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Alopecia areata, male pattern baldness and female pattern baldness
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220030007941%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20030007941&RS=DN/20030007941 US20030007941]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|2
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Androgenic alopecia (i.e. male pattern baldness), prostatic hyperplasia or both.
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220060009430%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20060009430&RS=DN/20060009430 US20060009430]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|3
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Inappropriate activation of the androgen receptor, acne, oily skin, alopecia
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220060009427%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20060009427&RS=DN/20060009427 US20060009427]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|4
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Prostatic hyperplasia, prostatic cancer, hirsutism, acne, male pattern baldness, seborrhea, and other diseases related to androgen hyperactivity
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050118282%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050118282&RS=DN/20050118282 US20050118282]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|5
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Alopecia, acne, oily skin, prostrate cancer, hirsutism, and benign prostate hyperplasia
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050085467%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050085467&RS=DN/20050085467 US20050085467]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|6
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Androgen-associated hair loss and androgen-skin related disorders.
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220060009429%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20060009429&RS=DN/20060009429 US20060009429]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|7
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Androgenetic or androgenic alopecia or androgeno-genetic alopecia
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220030073616%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20030073616&RS=DN/20030073616 US20030073616]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|8
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Diseases caused by testosterone (male-pattern alopecia)
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://v3.espacenet.com/textdoc?DB=EPODOC&IDX=EP0279010&F=0 EP0279010]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|9
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Alopecia areata, female pattern hair loss, hair loss secondary to chemotherapy or radiation treatment, stress-related hair loss, self-induced hair loss, scarring alopecia, and alopecia in non-human mammal
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220040157856%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20040157856&RS=DN/20040157856 US20040157856]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|10
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Male pattern alopecia
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050053572%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050053572&RS=DN/20050053572 US20050053572]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|11
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Alopecia, androgenic alopecia
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220060052405%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20060052405&RS=DN/20060052405 US20060052405]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|12
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Hair loss
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050123577%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050123577&RS=DN/20050123577 US20050123577]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|13
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Male pattern alopecia
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=6447762.PN.&OS=PN/6447762&RS=PN/6447762 US6447762]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|14
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Androgenetic, androgenic or androgenogenetic alopecia
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220040071647%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20040071647&RS=DN/20040071647 US20040071647]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|15
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Curing other scalp related problems
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050244362%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050244362&RS=DN/20050244362 US20050244362]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|16
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Patents by application ===
| + | |
| − | [[Image:application.jpg|thumb|center|700px|Distribution of patents based on application]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Signaling Pathway and linkages ===
| + | |
| − | [[Image:Slide1.GIF|thumb|center|700px|Alopecia pathways]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Players of Wnt inhibition Pathway == [[Image:wnt.jpg|thumb|right|600px|Wnt inhibition]]
| + | |
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="15", style="#008080"
| + | |
| − | !width="70" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Patent no.'''
| + | |
| − | !width="20" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Key compound'''
| + | |
| − | !width="70" bgcolor=DodgerBlue|'''Players of inhibition'''
| + | |
| − | |- style="height:10px"
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=lightyellow|[http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=6664247.PN.&OS=PN/6664247&RS=PN/6664247 US6664247]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=lightyellow|Pyrazole compounds
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=lightyellow|GSK3
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=lightyellow|[http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=6989385.PN.&OS=PN/6989385&RS=PN/6989385 US6989385]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=lightyellow|Pyrazole compounds
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=lightyellow|GSK3
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=lightyellow|[http://v3.espacenet.com/textdoc?DB=EPODOC&IDX=WO2005012256&F=0 WO2005012256]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=lightyellow|Pyrazole compounds
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=lightyellow|CDK,GSK3
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=6974819.PN.&OS=PN/6974819&RS=PN/6974819 US6974819]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Pyrimidine derivative
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|GSK3
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=6743791.PN.&OS=PN/6743791&RS=PN/6743791 US6743791]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Heterocyclic compounds
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|AKT3, GSK-3, ERK2
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220050277773%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20050277773&RS=DN/20050277773 US20050277773]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine derivatives
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|GSK3
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220040072836%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20040072836&RS=DN/20040072836 US20040072836]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Aza-oxindole derivatives
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|GSK3, AKT, PKC
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://v3.espacenet.com/textdoc?DB=EPODOC&IDX=EP1477489&F=0 EP1477489]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Pyrrolopyrimidine derivatives
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|GSK3
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://v3.espacenet.com/textdoc?DB=EPODOC&IDX=WO0056710&F=0 WO0056710]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|3-(Anilinomethylene) oxindoles
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|GSK3, AKT, PKC
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://v3.espacenet.com/textdoc?DB=EPODOC&IDX=WO03011287&F=0 WO2003011287]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Pyrazolon derivatives
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|GSK3, β-catenin
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=6924141.PN.&OS=PN/6924141&RS=PN/6924141 US6924141]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Lithium chloride, Wnt3/4/ 7
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|β-catenin, GSK3, Wnt
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=6706685.PN.&OS=PN/6706685&RS=PN/6706685 US6706685]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Peptide sequence
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|β-catenin
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=6683048.PN.&OS=PN/6683048&RS=PN/6683048 US6683048]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Peptide sequence
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|α-catenin, β-catenin
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=6677116.PN.&OS=PN/6677116&RS=PN/6677116 US6677116]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Peptide sequence LXXLL
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|β-catenin
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|[http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=6303576.PN.&OS=PN/6303576&RS=PN/6303576 US6303576]
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|Peptide sequence LXXLL
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=LightCyan|β-catenin
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | [[Image:coloury.jpg]]- '''Target sites and Details'''
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Pyrazole compounds ==
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | * '''Pyrazole''' (C3H4N2) refers both to the class of simple aromatic ring organic compounds of the heterocyclic series characterized by a 5-membered ring structure composed of three carbon atoms and two nitrogen atoms in adjacent positions and to the unsubstituted parent compound. Being so composed and having pharmacological effects on humans, they are classified as alkaloids although they are not known to occur in nature.
| + | |
| − | * Pyrazoles are produced synthetically through the reaction of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes with hydrazine and subsequent dehydrogenation
| + | |
| − | [[Image:pyrazole1.jpg|thumb|center|500px|Pyrazole (C3H4N2)]]
| + | |
| − | * Pyrazoles are used for their analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, antiarrhythmic, tranquilizing, muscle relaxing, psychoanaleptic, anticonvulsant, monoamineoxidase inhibiting, antidiabetic and antibacterial activities.
| + | |
| − | * Structurally related compounds are pyrazoline and pyrazolidine.
| + | |
| − | [[Image:pyrazole2.jpg|thumb|center|500px|Structurally related compounds]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === GSK3 inhibition by pyrazole compounds ===
| + | |
| − | [[Image:bold3.jpg]]
| + | |
| − | {| border="1" cellpadding="2", style="#008080"
| + | |
| − | !width="100"|[http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?TERM1=6989385+&Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=0&f=S&l=50 US6989385]
| + | |
| − | [[Image:US6989385.jpg]]
| + | |
| − | !width="100"|[http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=6664247.PN.&OS=PN/6664247&RS=PN/6664247 US6664247]
| + | |
| − | [[Image:US6664247.jpg]]
| + | |
| − | !width="100"|[http://v3.espacenet.com/textdoc?DB=EPODOC&IDX=WO2005012256&F=0 WO2005012256]
| + | |
| − | [[Image:WO2005012256.jpg]]
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=lightcyan|R1=T-Ring D, wherein
| + | |
| − | T is a valence bond and
| + | |
| − | Ring D = 5-6 membered aryl or heteroaryl ring;
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | R2 = hydrogen or C1-4 aliphatic and
| + | |
| − | R2'= hydrogen;
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | R3 = -R, -OR, or -N(R4)2, wherein
| + | |
| − | R = hydrogen, C1-6 aliphatic, 5-6 membered heterocyclyl, phenyl, or 5-6 membered heteroaryl, and
| + | |
| − | L is -O-, -S-, or -NH-; and
| + | |
| − | Ring D is substituted by up to three substituents selected from -halo, -CN, -NO2, -N(R4)2, optionally substituted C1-6 aliphatic group, -OR, -C(O)R, -CO2R, -CONH(R<4>), -N(R4)COR, -N(R4)CO2R, -SO2N(R4)2, -N(R4)SO2R, -N(R6)COCH2N(R4)2, -N(R6)COCH2CH2N(R4)2, or -N(R6)COCH2CH2CH2N(R4)2, wherein R = hydrogen, C1-6 aliphatic, phenyl, 5-6 membered heteroaryl ring, or 5-6 membered heterocyclic ring
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | |bgcolor=lightcyan|X = R1-A-NR4- or a 5- or 6-membered carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring; A is a bond, S02, C=O, NRg(C=O) or O(C=O) wherein Rg is hydrogen or C1-4 hydrocarbyl optionally substituted by hydroxy or C1-4 alkoxy; Y is a bond or an alkylene chain of 1, 2 or 3 carbon atoms in length;
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | R1 is hydrogen; carbocyclic or heterocyclic group having from 3 to 12 ring members; or C1-8 hydrocarbyl group optionally substituted by one or more substituents selected from halogen (e.g. fluorine), hydroxy, C1-4 hydrocarbyloxy, amino, mono- or di-C1-4 hydrocarbylamino, and carbocyclic or heterocyclic groups having from 3 to 12 ring members, and wherein 1 or 2 of the carbon atoms of the hydrocarbyl group may optionally be replaced by an atom or group selected from 0, S, NH, SO, S02;
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | R2 is hydrogen; halogen; C1-4 alkoxy (e.g. methoxy); or a C1-4 hydrocarbyl group optionally substituted by halogen (e.g. fluorine), hydroxyl or C1-4 alkoxy (e.g. methoxy); R3 is selected from hydrogen and carbocyclic and heterocyclic groups having from 3 to 12 ring members; and
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | R4 is hydrogen or a C1-4 hydrocarbyl group optionally substituted by halogen (e.g. fluorine), hydroxyl or C1-4 alkoxy (e.g. methoxy).
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | |bgcolor=lightcyan|X is a groupR1-A-NR4-or a 5-or 6-membered carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring;
| + | |
| − | A is a bond,SO2, C=O, NRg (C=O) or O(C=O) wherein Rg is hydrogen orC14 hydrocarbyl optionally substituted by hydroxy or C1-4 alkoxy;Y is a bond or an alkylene chain of 1,2 or 3 carbon atoms in length;R'is hydrogen; a carbocyclic or heterocyclic group having from 3 to 12 ring members; or a C1-8 hydrocarbyl group optionally substituted by one or more substituents selected from halogen (e. g. fluorine), hydroxy, C1-4 hydrocarbyloxy, amino, mono-ordi-Cl 4 hydrocarbylamino, and carbocyclic or heterocyclic groups having from 3 to 12 ring members, and wherein 1 or 2 of the carbon atoms of the hydrocarbyl group may optionally be replaced by an atom or group selected fromO, S, NH, SO, SO2 ;R2 is hydrogen; halogen;C14 alkoxy (e. g. methoxy); or aC14 hydrocarbyl group optionally substituted by halogen (e. g. fluorine), hydroxyl orC14 alkoxy (e. g. methoxy);R3 is selected from hydrogen and carbocyclic and heterocyclic groups having from 3 to 12 ring members; andR4 is hydrogen or a C1-4 hydrocarbyl group optionally substituted by halogen (e. g. fluorine), hydroxyl or C1-4 alkoxy (e. g. methoxy).
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Inhibition by amine derivatives ===
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''Patent Number''': US6989385
| + | |
| − | '''Applicant''': ''Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated''
| + | |
| − | '''Title''': Pyrazole compounds useful as protein kinase inhibitors
| + | |
| − | '''Basic Structure''':
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | [[Image:pyrazol1.jpeg]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''Derivatives of pyrimidine-pyrazole amine disclosed in the patent:'''
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | * [6-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)-2-(naphthalen-2-ylsulfanyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-met- hyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [6-(2-Methylphenyl)-2-(naphthalen-2-ylsulfanyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-- 2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Acetamido-phenylsulfanyl)-6-phenyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-pyra- zol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Isobutyrylylamino-phenylsulfanyl)-6-phenylpyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-- 2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-
| + | |
| − | * [6-(4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-methylsulfanyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-- pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-[6-phenyl-2-(4-propionylamino-phenylsulfanyl)-p- yrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Cyclopropanecarbonylamino-phenylsulfanyl)-6-phenylpyrimidin-4-yl]-(5- -methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-{6-phenyl-2-[4-(propane-1-sulfonylamino)-phenyl- sulfanyl]-pyrimidin-4-yl}-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Ethanesulfonylamino-phenylsulfanyl)-6-phenyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-meth- yl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Acetamidophenyl-sulfanyl)-6-(2-methylphenyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-meth- yl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Isobutanecarbonylamino-phenyl-sulfanyl)-6-phenyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-- methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Acetamido-phenyl-sulfanyl)-5-methyl-6-phenyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-meth- yl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Acetamido-phenyl-sulfanyl)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-me- thyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [6-(3-Acetamidophenyl)-2-(4-acetamido-phenyl-sulfanyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-- methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Isopropanesulfonylamino-phenyl-sulfanyl)-6-phenyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5- -methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * {2-[4-(2-Dimethylamino-acetylamino)-phenylsulfanyl]-6-phenyl-pyrimidin-4-y- l}-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(3-Chloro-benzylsulfanyl)-6-morpholin-4-yl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H- -pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(3-Chloro-benzylsulfanyl)-6-(2-methoxy-ethylamino)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-m- ethyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-Benzylsulfanyl-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-- pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-Benzylsulfanyl-6-morpholin-4-yl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-- yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(3-Chloro-benzylsulfanyl)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5- -methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-methoxy-benzylsulfanyl)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(- 5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Acetamido-phenyl-sulfanyl)-6-tert-butyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H- -pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Cyclopropyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-[6-phenyl-2-(4-propionylamino-phenyl-sulfa- nyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(3-Chloro-benzylsulfanyl)-6-(piperidin-1-yl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-- 2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-{2-[4-(morpholinesulfonyl)-benzylsulfanyl]-6-mo- rpholin-4-yl-pyrimidin-4-yl}-amine
| + | |
| − | * {6-(2-Methoxy-ethylamino)-2-[4-(morpholinesulfonyl)-benzylsulfanyl]-pyrimi- din-4-yl}-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * {6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-[4-(morpholinesulfonyl)-benzylsulfanyl]-pyri- midin-4-yl}-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [6-Methoxymethyl-2-(4-propionylamino-phenyl-sulfanyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-m- ethyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Methoxycarbonyl-phenyl-sulfanyl)-6-methoxymethyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-- methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(3,5-Dimethoxy-benzylsulfanyl)-6-morpholin-4-yl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-meth- yl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(3,5-Dimethoxy-benzylsulfanyl)-6-pyrrolidin-4-yl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-met- hyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * 5-Methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-[6-morpholin-4-yl-2-(naphthalene-2-ylmethylsulf- anyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * {2-(4-Acetamido-phenyl-sulfanyl)-6-[4-(3-dimethylamino-propoxy)-phenyl]-py- rimidin-4-yl}-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Acetamidophenylsulfanyl)-6-(morpholin-4-yl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methy- l-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [6-Hydroxymethyl-2-(4-propionylamino-phenyl-sulfanyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-m- ethyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Acetamido-phenyl-sulfanyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl- )-amine
| + | |
| − | * [6-(1-Butoxycarbonyl)-2-(4-propionylamino-phenyl-sulfanyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]- -(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [6-Methoxycarbonyl-2-(4-propionylamino-phenyl-sulfanyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5- -methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-(6-phenyl-2-phenylamino-pyrimidin-4-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Cyclopropyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-(6-phenyl-2-phenylamino-pyrimidin-4-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Cyclopropyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-[2-(3-methylphenylamino)-6-phenyl-pyrimidi- n-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-cyanomethylphenylamino)-6-phenyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-cyclopropyl-2H-p- yrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Cyclopropyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-[6-phenyl-2-(pyridin-3-ylmethylamino)-pyri- midin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(3-Chlorophenyl)amino-6-(3-nitrophenyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-py- razol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(3-Chlorophenyl)amino-6-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-met- hyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-[2-(4-sulfamoylphenylamino)-6-(3,4,5-trimethoxy- phenyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Chlorophenyl)amino-6-methyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-[5-(furan-2-yl)-2H-pyraz- ol-3-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(Benzimidazol-2-ylamino-)6-ethyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3- -yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Chlorophenyl)amino-6-methyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-phenyl-2H-pyrazol-3-y- l)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Chlorophenyl)amino-6-ethyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl- )-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-tert-Butyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-[2-(3-chlorophenyl)amino-6-(3-nitrophenyl)-- pyrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(3-Chlorophenyl)amino-6-(3-nitrophenyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-phenyl-2H-py- razol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [5-(Furan-2-yl)-2H-pyrazol-3-yl]-(6-phenyl-2-phenylamino-pyrimidin-4-yl)-a- mine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(Benzimidazol-2-ylamino)-6-methyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-phenyl-2H-pyrazol-- 3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(Benzimidazol-2-ylamino)-6-methyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-[5-(Furan-2-yl)-2H-py- razol-3-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Chlorophenylamino)-6-methyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-y- l)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Chlorophenyl)amino-5,6-dimethyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol- -3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5,6-Dimethyl-2-phenylamino-pyrimidin-4-yl)-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Chlorophenyl)amino-6-methoxymethyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-pyra- zol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(Benzimidazol-2-ylamino)-6-methoxymethyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-p- yrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (6-Methoxymethyl-2-phenylamino-pyrimidin-4-yl)-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-- amine
| + | |
| − | * (6-Methyl-2-phenylamino-pyrimidin-4-yl)-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(2-Chlorophenoxymethyl)-6-methyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-phenyl-2H-pyrazol-3- -yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(2-Chlorophenoxymethyl)-6-methyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-[5-(furan-2-yl)-2H-pyr- azol-3-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * (6-methyl-2-phenoxymethyl-pyrimidin-4-yl)-(5-phenyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [5-(Furan-2-yl)-2H-pyrazol-3-yl]-(6-methyl-2-phenoxymethyl-pyrimidin-4-yl)- -amine
| + | |
| − | * [5-(Furan-2-yl)-2H-pyrazol-3-yl]-(6-methyl-2-phenylsulfanylmethyl-pyrimidin-4-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [6-Methyl-2-(4-methyl-phenylsulfanylmethyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-phenyl-2H-p- yrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [5-(Furan-2-yl)-2H-pyrazol-3-yl]-[6-Methyl-2-(4-methyl-phenylsulfanylmethy- l)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Fluoro-phenoxymethyl)-6-methyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-phenyl-2H-pyrazol-- 3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Fluoro-phenoxymethyl)-6-methyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-[5-(furan-2-yl)-2H-py- razol-3-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * (6-Ethyl-2-phenylsulfanylmethyl-pyrimidin-4-yl)-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)- -amine
| + | |
| − | * (6-Ethyl-2-phenoxymethyl-pyrimidin-4-yl)-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [6-Ethyl-2-(4-fluorophenoxymethyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-- yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [6-Ethyl-2-(1-methyl-1-phenyl-ethyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-- 3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Chlororophenoxymethyl)-6-methyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-phenyl-2H-pyrazol- -3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Chlororophenoxymethyl)-6-methyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol- -3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Chlororophenoxymethyl)-6-methoxymethyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-- pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Chlororophenoxymethyl)-6-methyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-[5-(furan-2-yl)-2H-p- yrazol-3-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-(2-phenylsulfanylmethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-quin- azolin-4-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Methylphenylsulfanylmethyl)-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-cycloheptapyrimidi- n-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(1-Methyl-1-phenyl-ethyl)-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-cycloheptapyrimidin-4-y- l]-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(2,6-Dichlorobenzyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-quinazolin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-p- yrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [7-Benzyl-2-(2,6-dichlorobenzyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidin-- 4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [6-Benzyl-2-(4-chlorophenoxymethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-pyrido[4,3-d]pyrimi- din-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Chlorophenoxymethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-pyrido[4,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]- -(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(2,6-Dichlorobenzyl)-6-methyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl- )-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(2,6-Dichlorobenzyl)-5,6-dimethyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-- 3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | ----
| + | |
| − | '''Patent Number''': US7008948
| + | |
| − | '''Applicant''': Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated
| + | |
| − | '''Title''': Fused pyrimidyl pyrazole compounds useful as protein kinase inhibitors
| + | |
| − | '''Basic Structure'''
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | [[Image:pyrazol2.jpeg]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''Derivatives of pyrimidine-pyrazole amine disclosed in the patent:'''
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | * [2-(2-Clorophenyl)-5,6-dimethylpyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-Methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-- amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(2-Chloro-phenyl)-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-cycloheptapyrimidin-4-yl]-(1H-i- ndazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Fluoro-1H-indazol-3-yl)-[2-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydr- o-pyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]-
| + | |
| − | * [2-(2-Chloro-phenyl)-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-cycloheptapyrimidin-4-yl]-(7-fl- uoro-1H-indazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(2-Chloro-phenyl)-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-cycloheptapyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-fl- uoro-1H-indazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(2-Chloro-phenyl)-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-cycloheptapyrimidin-4-yl]-(5,7-- difluoro-1H-indazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (7-Fluoro-1H-indazol-3-yl)-[2-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydr- oquinazolin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Fluoro-1H-indazol-3-yl)-[2-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydr- oquinazolin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5,7-Difluoro-1H-indazol-3-yl)-[2-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetra- hydroquinazolin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Trifluoromethyl-1H-indazol-3-yl)-[2-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-5,6,7,8-- tetrahydroquinazolin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5,7-difluoro-1H-indazol-3-yl)-[2-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-6,7,8,9-tetra- hydro-5H-cycloheptapyrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * (6-Benzyl-2-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-pyrido[4,3-d]pyr- imidin-4-yl)-(5-fluoro-1H-indazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (1H-Indazol-3-yl)-[2-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-cycl- oheptapyrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * (7-Fluoro-1H-indazol-3-yl)-[2-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-6,7,8,9-tetrahydr- o-5H-cycloheptapyrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Fluoro-1H-indazol-3-yl)-[2-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-6,7,8,9-tetrahydr- o-5H-cycloheptapyrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Fluoro-1H-indazol-3-yl)-[2-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydr- o-pyrido[4,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * (1H-indazol-3-yl)-[2-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydroquinazol- in-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * (7-Benzyl-2-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-pyrido[4,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)-(5-fluoro-1H-indazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (1H-Indazol-3-yl)-[6-methyl-2-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * 1H-Indazol-3-yl)-[6-phenyl-2-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | ----
| + | |
| − | '''Patent Number''': US6977262
| + | |
| − | '''Assignee''': Mitsubishi Pharma Corporation
| + | |
| − | '''Title''': Dihydropyrazolopyridine compounds and pharmaceutical use thereof
| + | |
| − | '''Basic Structure''':
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | [[Image:pyrazol3.jpeg]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''Derivatives of pyrimidine-pyrazole amine disclosed in the patent:'''
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | * Ethyl 4-(2-chlorophenyl)-4,7-dihydro-6-methyl-2H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate
| + | |
| − | * Ethyl 4,7-dihydro-4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-6-methyl-2H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate
| + | |
| − | * Ethyl 4,7-dihydro-6-methyl-4-(2-trifluoromethylphenyl)-2H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridin e-5-carboxylate
| + | |
| − | * Methyl 4-(2-chlorophenyl)-4,7-dihydro-6-methyl-2H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate
| + | |
| − | * t-Butyl 4-(2-chlorophenyl)-4,7-dihydro-6-methyl-2H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate
| + | |
| − | * Isopropyl 4-(2-fluorophenyl)-4,7-dihydro-6-methyl-2H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate
| + | |
| − | * Benzyl 4-(2-chlorophenyl)-4,7-dihydro-6-methyl-2H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate
| + | |
| − | * 4-(2-Chlorophenyl)-5-dimethylaminocarbonyl-4,7-dihydro-6-methyl-2H-pyrazolo [3,4-b]pyridine
| + | |
| − | * 4-(2-Chlorophenyl)-5-hydrazinocarbonyl-4,7-dihydro-6-methyl-2H-pyrazolo[3,4 -b]pyridine
| + | |
| − | * 4-(2-Fluorophenyl)-4,7-dihydro-6-methyl-5-isopropylthiocarbonyl-2H-pyrazolo [3,4-b]pyridine
| + | |
| − | * 4,7-Dihydro-6-methyl-5-nitro-4-(2-trifluoromethylphenyl)-2H-pyrazolo[3,4-b] pyridine
| + | |
| − | * Ethyl 4,7-dihydro-4-phenyl-6-trifluoromethyl-2H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carbox ylate
| + | |
| − | * Ethyl 4-(2-fluorophenyl)-4,7-dihydro-6-trifluoromethyl-2H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridin e-5-carboxylate
| + | |
| − | * Ethyl 4-(2-chlorophenyl)-4,7-dihydro-6-trifluoromethyl-2H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridin e-5-carboxylate maleate
| + | |
| − | * Ethyl 4,7-dihydro-4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-6-trifluoromethyl-2H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridi ne-5-carboxylate
| + | |
| − | * Ethyl 4,7-dihydro-6-trifluoromethyl-4-(2-trifluoromethylphenyl)-2H-pyrazolo[3,4- b]pyridine-5-carboxylate
| + | |
| − | * Ethyl 4-(3-chlorophenyl)-4,7-dihydro-6-trifluoromethyl-2H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridin e-5-carboxylate
| + | |
| − | ----
| + | |
| − | '''Patent Number''': US6664247
| + | |
| − | '''Assignee''': Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated
| + | |
| − | '''Title''': Pyrazole compounds useful as protein kinase inhibitors'''
| + | |
| − | '''Basic Structure''':
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | [[Image:pyrazol4.jpeg]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''Derivatives of pyrimidine-pyrazole amine disclosed in the patent:'''
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | * (5-Cyclopropyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-[2-(naphtalen-2-ylsulfanyl)-6-phenylpyrimid in-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * 5-Cyclopropyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-[2-(3-methoxycarbonyl-phenylylsulfanyl)-6-p henylpyrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Cyclopropyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-[2-(naphthalen-2-ylsulfanyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl ]-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Cyclopropyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-[5,6-dimethyl-2-(naphthalen-2-ylsulfanyl)-p yrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Cyclopropyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-[5-methyl-2-(naphthalen-2-ylsulfanyl)-pyrim idin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Cyclopropyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-[6-methyl-2-(naphthalen-2-ylsulfanyl)-pyrim idin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Cyclopropyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-[6-(morpholin-4-yl)-2-(naphthalen-2-ylsulfa nyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Cyclopropyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-[6-(1-methylpiperazin-4-yl)-2-(naphthalen-2 -ylsulfanyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * [6-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)-2-(naphthalen-2-ylsulfanyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-meth yl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [6-(2-Methylphenyl)-2-(naphthalen-2-ylsulfanyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2 H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Acetamido-phenylsulfanyl)-6-phenyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-pyraz ol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-[2-(naphthalen-2-ylsulfanyl)-6-phenyl-pyrimidin- 4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Isobutyrylylamino-phenylsulfanyl)-6-phenylpyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2 H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [6-(4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-methylsulfanyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-p yrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-[6-phenyl-2-(4-propionylamino-phenylsulfanyl)-py rimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Cyclopropanecarbonylamino-phenylsulfanyl)-6-phenylpyrimidin-4-yl]-(5- methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-{6-phenyl-2-[4-(propane-1-sulfonylamino)-phenyls ulfanyl]-pyrimidin-4-yl}-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Ethanesulfonylamino-phenylsulfanyl)-6-phenyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methy l-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Acetamidophenyl-sulfanyl)-6-(2-methylphenyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methy l-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Isobutanecarbonylamino-phenyl-sulfanyl)-6-phenyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-m ethyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Acetamido-phenyl-sulfanyl)-5-methyl-6-phenyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methy l-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Acetamido-phenyl-sulfanyl)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-met hyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [6-(3-Acetamidophenyl)-2-(4-acetamido-phenyl-sulfanyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-m ethyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Isopropanesulfonylamino-phenyl-sulfanyl)-6-phenyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5- methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (2-[4-(2-Dimethylamino-acetylamino)-phenylsulfanyl]-6-phenyl-pyrimidin-4-yl }-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(3-Chloro-benzylsulfanyl)-6-morpholin-4-yl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H- pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(3-Chloro-benzylsulfanyl)-6-(2-methoxy-ethylamino)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-me thyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-Benzylsulfanyl-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-p yrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-Benzylsulfanyl-6-morpholin-4-yl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-y l)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(3-Chloro-benzylsulfanyl)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5- methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-methoxy-benzylsulfanyl)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5 -methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Acetamido-phenyl-sulfanyl)-6-tert-butyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H- pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * 5-Cyclopropyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-[6-phenyl-2-(4-propionylamino-phenyl-sulfan yl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(3-Chloro-benzylsulfanyl)-6-(piperidin-1-yl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2 H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-{2-[4-(morpholinesulfonyl)-benzylsulfanyl]-6-mor pholin-4-yl-pyrimidin-4-yl}-amine
| + | |
| − | * {6-(2-Methoxy-ethylamino)-2-[4-(morpholinesulfonyl)-benzylsulfanyl]-pyrimid in-4-yl}-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * {6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-[4-(morpholinesulfonyl)-benzylsulfanyl]-pyrim idin-4-yl}-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [6-Methoxymethyl-2-(4-propionylamino-phenyl-sulfanyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-me thyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Methoxycarbonyl-phenyl-sulfanyl)-6-methoxymethyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-m ethyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(3,5-Dimethoxy-benzylsulfanyl)-6-morpholin-4-yl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methy l-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(3,5-Dimethoxy-benzylsulfanyl)-6-pyrrolidin-4-yl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-meth yl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5-Methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-[6-morpholin-4-yl-2-(naphthalene-2-yl-methylsulf anyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * {2-(4-Acetamido-phenyl-sulfanyl)-6-[4-(3-dimethylamino-propoxy)phenyl]-pyri midin-4-yl}-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Acetamidophenylsulfanyl)-6-(morpholin-4-yl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl -2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [6-Hydroxymethyl-2-(4-propionylamino-phenyl-sulfanyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-me thyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(4-Acetamido-phenyl-sulfanyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl) -amine
| + | |
| − | * [6-(1-Butoxycarbonyl)-2-(4-propionylamino-phenyl-sulfanyl)pyrimidin-4-yl]-( 5-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [6-Methoxycarbonyl-2-(4-propionylamino-phenyl-sulfanyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5- methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-amine.
| + | |
| − | ----
| + | |
| − | '''Patent Number''': US2004224944
| + | |
| − | '''Assignee''': VERTEX PHARMACEUTICALS INC
| + | |
| − | '''Title''': Pyrazole compounds useful as protein kinase inhibitors
| + | |
| − | '''Basic Structure''':
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | [[Image:pyrazol5.jpeg]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''Derivatives of pyrimidine-pyrazole amine disclosed in the patent:'''
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | * [2-(2-Chloro-phenyl)-6,7-dihydro-5H-cyclopentapyrimidin-4-yl]-(5,7-difluoro-1H-indazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (1H-Indazol-3-yl)-[2-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-5,6,7,8,9,10-hexahydro-cyclooctapyrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * (7-Fluoro-1H-indazol-3-yl)-[2-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-5,6,7,8,9,10-hexahydro-cyclooctapyrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * (5,7-Difluoro-1H-indazol-3-yl)-[2-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-5,6,7,8,9,10-hexahydro-cyclooctapyrimidin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * [6-Cyclohexyl-2-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(1H-indazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [6-(2-Fluoro-phenyl)-2-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-(1H-indazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * (6-Fluoro-1H-indazol-3-yl)-[2-(2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-quinazolin-4-yl]-amine
| + | |
| − | * 3-[2-(2-Trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-quinazolin-4-ylamino]-1H-indazole-5-carboxylic acid methyl ster
| + | |
| − | * (5-Methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-[2-(2-naphthyl-1-yl)-quinazolin-4-yl]-
| + | |
| − | * [2-(2-Chloro-phenyl)-pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]-(7-fluoro-1H-indazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | * [2-(2-Chloro-phenyl)-pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]-(5-fluoro-1H-indazol-3-yl)-amine
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Other derivates for alopecia ===
| + | |
| − | [[Image:other derivates.jpeg]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Inhibition of 5- - reductase by Finasteride ==
| + | |
| − | [[Image:5-alpha-reductase inhibition.jpeg]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Structure-Activity Relationships(SARs) ===
| + | |
| − | [[Image:SAR_map.gif]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Questions Dolcera Answers ==
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''What’s hot?'''
| + | |
| − | * What compositions/ approaches are the most promising?
| + | |
| − | * What can I license?
| + | |
| − | * Can you map blockbuster products to their patents?
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''Can you save me some time?'''
| + | |
| − | * What combinations/ compounds have already been tried?
| + | |
| − | * Is any empirical data available?
| + | |
| − | * Can you tell me the side effects?
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''Where should I focus my R&D investment?'''
| + | |
| − | * What are the most promising approaches?
| + | |
| − | * Where’s the ‘white space’ for me to play in?
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''Any hints for research?'''
| + | |
| − | * Are there any combinations I could develop?
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''What should I do in this geography?'''
| + | |
| − | * What are my competitors up to in this geography?
| + | |
| − | * What are my strengths/ weaknesses here?
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''What’s my competition up to?'''
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | * What’s my top competitor investing in?
| + | |
| − | * Are there any loopholes in their patents?
| + | |
| − | * When are their patents expiring?
| + | |
| − | * Will a competitor emerge from nowhere and surprise me?
| + | |
| − | * What are the crowded areas?
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''How do I play defense?'''
| + | |
| − | * What should my blocking/reactive strategies be?
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == New Combinations based on IP study? ==
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | Yes, new Combinations can be made with '''natural products''' based on IP study
| + | |
| − | * Walnut extract containing [[Image:5ar.jpg]] inhibitor (as anti-androgen) and Flavnones (for vasodilation).
| + | |
| − | * Sophora Flavnones (for vasodilation) in combination with Saw Palmetto berry (as anti-androgen).
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''Note:''' The above combinations are based on limited study and are only possible examples
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == IP studies provides ==
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === Technology trends ===
| + | |
| − | * Use of saw palmetto berry for treating alopecia was first patented in 1996.
| + | |
| − | * Since then, 144 patents (including family patents) have been filed till 2006.
| + | |
| − | * Most patents use saw palmetto berry in combination with other products.
| + | |
| − | [[Image:Technology1.jpg|thumb|center|700px|Technology trends]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | === New opportunities ===
| + | |
| − | Yes, the IP studies provide new opportunities in the following area.
| + | |
| − | * Sophora Flavescens contain flavnoids.
| + | |
| − | * Natural extract Sophora Flavescens cited in LG patent of 2001.
| + | |
| − | * Research shows fewer than 7 patents based on Sophora Flavescens for hair loss or alopecia.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | * What's this?
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == GSK-3 Inhibition==
| + | |
| − | * In the canonical Wnt signaling cascade, adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), axin, and GSK3 constitute the so-called destruction complex, which controls the stability of beta-catenin. It is generally believed that four conserved Ser/Thr residues in the N terminus of beta-catenin are the pivotal targets for the constitutively active serine kinase GSK3. GSK3 covalently modifies beta-catenin by attaching phosphate groups (from ATP) to serine, and threonine residues. In so doing, the functional properties of the protein kinase’s substrate (beta-catenin) are modified.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | * In the absence of Wnt signals, glycogen synthase kinase (GSK) is presumed to phosphorylate the N-terminal end of beta-catenin, thus promote degradation of beta-catenin and subsequent ubiquitination and proteasomal targeting.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | * Wnt signaling inhibits GSK3 activity. As a consequence, beta-catenin would no longer be phosphorylated and accumulate to form nuclear complexes with TCF/LEF factors.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | [[More details on GSK-3]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''Key points'''
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | * Beta-catenin phosphorylation at serine 45 (Ser45), threonine 41 (Thr41), Ser37, and Ser33 is critical for beta-catenin degradation. [http://jb.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/132/5/697 source]
| + | |
| − | * Regulation of beta-catenin phosphorylation is a central part of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. [http://content.karger.com/ProdukteDB/produkte.asp?Aktion=ShowPDF&ProduktNr=223838&ArtikelNr=66755&filename=66755.pdf source]
| + | |
| − | * Ser-X-X-X-Ser (X is any amino acid) motif is obligatory for beta-catenin phosphorylation by GSK3.[http://lib.bioinfo.pl/auth:He,X source]
| + | |
| − | * Beta-catenin phosphorylation/degradation and its regulation by Wnt can occur normally in the absence of Thr41 as long as the Ser-X-X-X-Ser motif/spacing is preserved. [http://pubs.acs.org/cgi-bin/abstract.cgi/bichaw/2006/45/i16/abs/bi0601149.html source]
| + | |
| − | * GSK3’s substrate specificity is unique in that phosphorylation of substrate only occurs if a phosphoserine or phosphotyrosine is present four residues C-terminal to the site of GSK phosphorylation. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=11430833&dopt=Abstract source]
| + | |
| − | * A phosphorylation cascade starts from GSK3 itself and initiates it in beta-catenin. [http://www.genesdev.org/cgi/content/full/16/16/2073 source]
| + | |
| − | * Thus our goal is to stop the phosphorylation of the serine and threonine residue of GSK3.
| + | |
| − | * The figure below illustrates the phosphorylation mechanism of serine and threonine by ATP.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | [[image:GSK3_phosphorylation.jpg|400 px|center|thumb|Phosphorylation mechanism]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | * The common phosphorylation procedure through ATP to ADP conversion we can’t stop.
| + | |
| − | * Thus we have to target on the Oxygen atom at the Phosphorous group, marked in the red circles in the figure above. As oxygen is a Lewis acid with strong electron donating capacity, so usually a strong electron pair acceptor can easily bind to oxygen atom and preventing phosphorylation
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | '''Serine - pyrazole reaction'''
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | [[image:serine-pyrazol.jpg|600 px|center|thumb|Serine and Pyrazole reactio]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Conclusions ==
| + | |
| − | * Hair loss medication is a very active area of research and intellectual property development.
| + | |
| − | * One of the most promising areas of development is the area of Anti-androgens.
| + | |
| − | * The top companies are Merck, L’Oreal and Smithkline.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Useful links ==
| + | |
| − | * [http://www.biocarta.com/pathfiles/h_ghPathway.asp Pathways example]
| + | |
| − | * [http://www.cellsignal.com/category.asp?catalog_name=CellSignal&category_name=MAPK+Signaling Signaling Pathways]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == Summary ==
| + | |
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) has recently emerged, in the field of medicinal chemistry, as one of the most attractive therapeutic targets for the development of selective inhibitors as promising new drugs for numerous serious pathologies, including Alzheimer's disease, stroke, bipolar disorders, chronic inflammatory processes, cancer, alopecia and Type II diabetes. The full potential of GSK-3 inhibitors is yet to be realised and the number of drug candidates being developed by both academic centres and pharmaceutical companies has increased exponentially in the last three years. This review discloses recent discoveries on peptides and small molecules targeting GSK-3. Antisense therapy for the modulation of GSK-3 expression is also discussed. Focusing attention on this exciting target could thus reap considerable clinical and economic rewards. source
Prediction search done on NetPhos 2.0 server, which produces neural network predictions for serine, threonine and tyrosine phosphorylation sites in eukaryotic proteins.
GSK3B_HUMAN consists of 420 amino acids sequemnce.
Beta-catenin consists of 781 amino acid residue.