Difference between pages "Ureteral Stent" and "Pressure sensitive adhesives"
(→Dolcera Dashboard) |
(→Dashboard) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | ==Dashboard== | |
| − | ''' | + | Dolcera dashboard provides quick and easy navigation through the technology segments. Below is the snapshot of how it look like. Click on the link [http://www.dolcera.com/auth/dashboard/dashboard.php?workfile_id=262 '''Dolcera Dashboard'''] for Pressure Sensitive Adhesives. |
| − | + | [http://www.dolcera.com/auth/dashboard/dashboard.php?workfile_id=262 '''Dolcera Dashboard'''] | |
| − | + | [[image:dashboard.jpg|center|500 px]] | |
| − | == | + | ==Overview== |
| − | + | Pressure sensitive adhesive (PSA, self adhesive, self stick adhesive) is adhesive that forms a bond when pressure is applied to marry the adhesive with the adherend. No solvent, water, or heat is needed to activate the adhesive. It is used in pressure sensitive tapes, labels, note pads, automobile trim, and a wide variety of other products. | |
| − | + | As the name "pressure sensitive" indicates, the degree of bond is influenced by the amount of pressure which is used to apply the adhesive to the surface. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Surface factors such as smoothness, surface energy, removal of contaminants, etc. are also important to proper bonding. | |
| − | + | PSAs are usually designed to form a bond and hold properly at room temperatures. PSAs typically reduce or lose their tack at cold temperatures and reduce their shear holding ability at high temperatures: Specialty adhesives are made to function at high or low temperatures. It is important to choose an adhesive formulation which is designed for its intended use conditions. | |
| − | + | ===Surface Energy=== | |
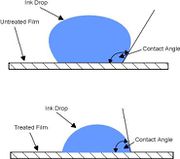
| + | [[Image:Surface energy.jpg|thumb|right|800|Measuring of Surface Energy]] | ||
| + | # Surface energy is a measure of how well an adhesive wets out over the surface of the material to which it is applied. | ||
| + | # The most common method of determining the surface energy is to measure the contact angle of a water droplet on the substrate surface. | ||
| + | # The contact angle between the solid and the fluid is the angle measured within the fluid, between the solid surface and the tangent plane to the liquid surface at the point of intersection. | ||
| + | # A contact angle of greater than 90° indicates that the fluid (which is ink or adhesive in this case) has not wet the surface. Conversely an angle of less than 90° means that the fluid has wet the surface - if the angle approaches zero then the surface is completely wetted by the fluid. | ||
| + | # The surface energy or the wetability of a particular substrate is measured in dynes/cm. [http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.pcn.org/images/Technical%2520Notes%2520-%2520Corona1.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.pcn.org/Technical%2520Notes%2520-%2520Corona.html&h=327&w=370&sz=13&hl=en&start=2&um=1&tbnid=Nb4kgRrPYnxojM:&tbnh=108&tbnw=122&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dsurface%2Benergy%26svnum%3D10%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26sa%3DX Source] | ||
| + | ===Low Surface Energy Substrates=== | ||
| + | # Low energy plastics, such as polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE) and Teflon (PTFE) are essentially "non- stick" plastics. | ||
| + | # Their molecular structure inhibits the adhesion and printing processes - this molecular structure is basically inert or inactive – these polymers are said to have a low surface energy. | ||
| + | # Materials with low surface energy (LSE) do not allow adhesives to wet out, while materials with high surface energy (HSE) provide excellent wet-out, providing the best adhesion. | ||
| + | # Rubber-based adhesives usually provide better adhesion to LSE surfaces. | ||
| + | # Some substrates require special treatment such as corona treating, primers, top coating, etc., in order to achieve better adhesion. | ||
| + | # On some LSE substrates, adhesion levels improve the longer adhesive is applied. [http://www.chemsultants.com/latestprods/adhesive_definitions.html Source] | ||
| − | + | ===Adhesion=== | |
| + | [[Image:Adhesionnew.jpg|thumb|right|800|Adhesion]] | ||
| + | # Adhesion is the molecular force of attraction between unlike materials. | ||
| + | # Adhesion and cohesion, attractive forces between material bodies. A distinction is usually made between an adhesive force, which acts to hold two separate bodies together (or to stick one body to another) and a cohesive force, which acts to hold together the like or unlike atoms, ions, or molecules of a single body. | ||
| + | # For example water molecules stick to each other. This is caused by hydrogen bonds that form between the slightly positive and negative ends of neighboring molecules. | ||
| + | # Water is found in drops; perfect spheres. It’s hard to imagine water behaving any other way due to cohesion and water molecules stick to other surfaces due to adhesion.[http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.ccs.k12.in.us/chsBS/kons/kons/images/water-droplet.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.ccs.k12.in.us/chsBS/kons/kons/physical_properties_of_water.htm&h=168&w=238&sz=15&hl=en&start=4&tbnid=UrmkX2TGv_os2M:&tbnh=77&tbnw=109&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dwater%2Badhesion%26gbv%3D2%26svnum%3D10%26hl%3Den%26sa%3DG Source] | ||
| − | = | + | ==Application of PSA== |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ===Application in electronics and electrical industry=== | |
| − | + | Electrical grade PSAs are critical components in the design many of today's electrical and electronic components in the electrical industry. The construction of this type of PSA is difficult since lower concentration of conductive filler must be used in order to prevent the drying out of polymer by the conductive filler, with attendant loss of tack. The conductivity of electrically conductive PSA in the direction of pressure action is to a certain extend depend on the direction of pressure applied [http://www.springerlink.com/content/j5448654801gg60q/ Florian, 2003] | |
| − | + | Electrical grade PSAs are designed and manufactured using materials using material that are physically and chemically stable in the presence of humidity and electrical stress. The acrylic high tack PSAs works very well in static and dynamic joints. The PSA agents are used in three forms i.e. modified aqueous dispersions or solutions in different solvents and as hot melts adhesives. PSA tapes find application in electronic assemblies [http://www.calce.umd.edu/articles/abstracts/2004/assemblies.htm Reliability of Pressure-Sensitive Adhesive Tapes for Heat Sink Attachment in Air-Cooled Electronic Assemblies] | |
| + | [[Image: PSA tapes.jpg|thumb|center|800px|[http://www.biztrademarket.com/User/166116/bb/insulation_tape_eho.jpg PSA tapes]]] | ||
| − | == | + | ===Application in automobile industry=== |
| − | + | While mechanical fasteners will always be the choice when maximum torque and linear force are required in automobile industry, pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSAs) can often provide a better method of joining or bonding than traditional screws, nuts, bolts, rivets and welds. | |
| + | The design, performance, and production reasons for replacing mechanical or fusion fastening methods with PSAs include, but are not limited to: | ||
| + | # Distributing stress over the entire bonded area: The concentrated stress of mechanical fasteners can be eliminated and design engineers can specify lighter, thinner materials without sacrificing durability and product integrity. | ||
| + | # Bonding dissimilar materials: The ability to bond two totally different substrates can yield a superior combination for product strength and performance. PSAs are an ideal counterbalance for varying factors of expansion between surfaces, such as laminating layers of metal. | ||
| + | # Maintaining assembled substrate integrity: Less machining and finishing means more latitude for design engineers and improved aesthetics for greater consumer appeal. | ||
| + | # Incorporating fatigue resistance: PSAs bring great flexibility, allowing for high extension and recovery under heavy loads. | ||
| + | # Durability by design: PSAs fill voids and gaps and can bond loose-fitting parts. | ||
| + | Increasing production efficiency: PSAs reduce material requirements, provide product weight reduction, require fewer assembly and finishing steps, and minimize training [http://www.flexcon.com/Resource-Center/~/media/Files/PDFs/Website/Resource%20Center/White%20Papers/design%20engineering%20aspects%20of%20pressure-sensitive%20adhesives.ashx FLEXcon white paper] | ||
| − | |||
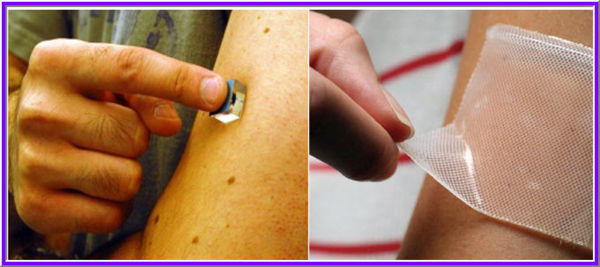
| + | ===Medical applications=== | ||
| − | + | There are two essential requirements of medical PSAs, that they should stick firmly to a difficult substrate (skin) and that they should be easily and cleanly removed from that substrate when desired. These requirements would seem to be in conflict: a high peel force usually signals the ability to stick firmly, while a low force is needed when removing dressings by peeling. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | A number of ways have been considered to resolve this conflict. These may be divided into two broad categories: those that make the best of existing PSA technology, broadly taking a physical approach, and those that introduce novel chemistry into the process. Physical approaches consider such details as the dependence of peel force on peel angle, peel rate, backing materials, the deformation of the skin during peeling and use of barrier films and solvents. As an alternative to simply making the best of the physics of the peeling process, various workers have devised chemical systems for making the adhesive less strongly adhering at the time of removal. These systems usually consist of introducing a ‘switch’ mechanism into a strongly adhering adhesive so that its adherence may be reduced significantly at the time of removal by operation of the ‘switch’. Means of activating the ‘switch’ include: heat (warming or cooling), application of water via an absorbent backing and exposure to visible light. These may produce physical or chemical changes in the adhesive [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6TW7-43W00T1-3&_user=10&_coverDate=12%2F31%2F2001&_alid=1598193691&_rdoc=3&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_origin=search&_zone=rslt_list_item&_cdi=5555&_st=13&_docanchor=&view=c&_ct=15397&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=17b33208ec83c0db321e3d3882e5ffe3&searchtype=a Chivers, 2001] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ===PSAs drive transdermal delivery=== | |
| − | + | Transdermal or through-the-skin delivery of drugs has assumed an important place in drug therapy, eliminating many of the shortcomings of syringes and pills. [http://www.adhesivesresearch.com/Pharmaceutical_ARx_LLC/Pharmaceutical/Component_Applications_And_Technologies/ActiveTransdermalDeliverySystems.aspx Active Transdermal Delivery Systems] The three most commonly used adhesives used for transdermal delivery are polyisobutylenes, polyacrylates and silicones [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6VJY-3WRB3HM-6&_user=10&_coverDate=02%2F01%2F1999&_rdoc=1&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_origin=search&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_searchStrId=1598124405&_rerunOrigin=google&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=f7968d61a743de54de6d04fb28c0cf00&searchtype=a Tan and Pfister, 1999] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | [[Image: Transdermal.jpg|thumb|center|600px|[http://www.qmed.com/files/ck_images/images/Nusil.jpg Delivery to skin]]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * In a typical '''disk drive''', PSAs are applied to the base casting to secure the motor-mounting flange and motor assembly | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Application in aerospace industry=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Aerospace manufacturers uses PSAs to assemble sheet-metal components into sub assemblies. The aerospace industry, primarily satellite manufacturers, have expressed the need for a low outgas, thermally stable, adhesive tape which can work at both high, 175ºC, and low, -100ºC, temperatures. New silicone PSA was fabricated to pass, low outgassing requirements of 1% or less Total Mass Loss (TML) and 0.1% or less Collectable Volatile Condensable Materials (CVCM) [http://www.polytec-pt.de/ger/_files/24_LowOutgasSiliconePressureSensitiveAdhesiveForAerospaceApplications2%281%29.pdf Riegler, 2005]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Making of PSAs== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Although PSPs can be obtained by different polymerization processes (i.e., emulsion, solution, hot-melt, or radiation curing), much attention has recently been devoted to the utilization of more environmentally friendly processes such as emulsion polymerization. Soft polymer networks are commonly used as previous termpressure sensitive adhesivesnext term (PSAs). This is due to their unique ability to deform and yet to resist flow. These contradictory requirements indicate that the mechanical properties are finely tuned, and that the types of deformation upon application are carefully considered. Variety of PSAs can be prepared by mixing a linear vinyl terminated polymer with a silane terminated f-functional cross-linker. [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6TW7-4VJ4WRW-1&_user=10&_coverDate=10%2F31%2F2009&_alid=1598127284&_rdoc=6&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_origin=search&_zone=rslt_list_item&_cdi=5555&_sort=r&_st=13&_docanchor=&view=c&_ct=20058&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=31aa31be0a41e917372805a44d352007&searchtype=a Jensen et al., 2009] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | {|border " | + | {|border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" align = "center" width="70%" |
| − | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''Sr. No.''' | |
| − | | | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''PSA process''' |
| − | | | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''Chemical composition''' |
| − | | | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''Time of launch''' |
| − | | | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''1''' |
| − | + | |align = "center"|'''Solvent-based''' | |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|Rubber/resin, acrylics, silicones |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|Since 19th century |
| − | | | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''2''' |
| − | + | |align = "center"|'''Hot-melt''' | |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|Block copolymers, acrylics |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|1940s |
| − | | | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''3''' |
| − | + | |align = "center"|'''Emulsion (water)-based''' | |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|Acrylics, natural and synthetic rubber, ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|1970s |
| − | | | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''4''' |
| − | + | |align = "center"|'''Radiation-cured''' | |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| Acrylics, rubber |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|1970s |
| − | | | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | {| | + | {|border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" align = "center" width="80%" |
| − | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''Sr. No.''' | |
| − | | | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''Properties''' |
| − | | | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''Solvent-based: acrylic''' |
| − | | | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''Hot-melt: styrene-isobutylene-styrene.''' |
| − | | | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''Emulsion based: acrylics''' |
| − | | | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''1''' |
| − | + | |align = "center"|PS performance | |
| + | |align = "center"|Excellent | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Excellent | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Very good | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''2''' |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|Ease of compounding |
| + | |align = "center"|Moderate | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Difficult | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Easy | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''3''' | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Formulation flexibility | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Limited | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Excellent | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Moderate | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''4''' | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Coating method flexibility | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Limited | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Poor | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Excellent | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''5''' | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Ease of changeover | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Limited | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Poor | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Excellent | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''6''' | ||
| + | |align = "center"|PSA reproducibility | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Excellent | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Limited | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Excellent | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''7''' | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Aging properties | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Excellent | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Poor | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Excellent | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''8''' | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Clarity/color | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Excellent | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Poor | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Excellent | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''9''' | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Safety/toxicity | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Poor | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Poor | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Excellent | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''10''' | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Raw material costs | ||
| + | |align = "center"|High | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Low | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Medium | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''11''' | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Coating/compounding costs | ||
| + | |align = "center"|High | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Medium | ||
| + | |align = "center"|Low | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| + | ===Effect of important parameters on PSA making and performance=== | ||
| + | ====Effect of polymer molecular weight and crosslinking reactions on the end-use properties of PSAs==== | ||
| + | In a study wherein polymer molecular weight and polymer microstructure were regulated using different chain transfer agent (CTA) concentrations and by addition of a diacrylic monomer (MM) it was shown that all of the measured adhesion properties strongly depend on molecular weight of the synthesized polymer and on the amount of gel phase [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6TW7-4SH0Y17-1&_user=10&_coverDate=03%2F31%2F2009&_alid=1598127284&_rdoc=8&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_origin=search&_zone=rslt_list_item&_cdi=5555&_sort=r&_st=13&_docanchor=&view=c&_ct=20058&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=0c2fe11851b57347e066ff78a975a690&searchtype=a Kajtna et al., 2009] | ||
| − | == | + | ====Effect of composition on Mechanical behaviours and fracture energy of PSAs==== |
| + | In a study it was shown that the mechanical behaviour depend on their composition but majority of fracture energy is dissipated on the first millimetre near the bending zone where fibrils elongation is maximum. Observations of interfaces between PSAs and glass substrate underline that fracture energy varies linearly according to the contact area [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6TW7-4N2D2V9-2&_user=10&_coverDate=12%2F31%2F2007&_alid=1598127284&_rdoc=16&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_origin=search&_zone=rslt_list_item&_cdi=5555&_sort=r&_st=13&_docanchor=&view=c&_ct=20058&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=6021375899d8929d9ec349bc3fd3c01d&searchtype=a Horgnies et al., 2007] | ||
| − | + | ====Effect of tackifier on PSAs==== | |
| + | To study the effect of tackifier (such as hydrogenated cyclo-aliphatic resin) a model system consisting of polystyrene-b-polyisoprene-b-polystyrene triblock copolymer was prepared. Tackifier increased the peel adhesion significantly and the increase became stronger above 40 wt% tackifier. The higher peel adhesion was obtained in the system with the larger amount of agglomerates of tackifier in the polyisoprene matrix. [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6TW7-4RJKX1T-1&_user=10&_coverDate=10%2F31%2F2008&_alid=1598155857&_rdoc=4&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_origin=search&_zone=rslt_list_item&_cdi=5555&_sort=r&_st=13&_docanchor=&view=c&_ct=18242&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=41c38a7bf066473704bf91918b843915&searchtype=a Sasaki et al., 2008] | ||
| − | + | ====Effect of chain transfer agent and cross-linker concentration in making of PSAs==== | |
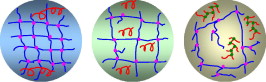
| − | + | In a study it was shown that a constant cross-linker concentration, one can manipulate the polymer micro-structure by adding varying amounts of chain transfer agent. Three examples of these micro-structures are depicted below which show a tight gel network with long-chain sol polymers, a loose gel network with shorter sol polymers, and an imperfect gel structure with highly branched sol polymers. By manipulating the micro-structure, previous termpressure-sensitive adhesivenext term performance can be affected. [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6TWW-4YG1M1T-3&_user=10&_coverDate=06%2F30%2F2010&_alid=1598155857&_rdoc=10&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_origin=search&_zone=rslt_list_item&_cdi=5573&_sort=r&_st=13&_docanchor=&view=c&_ct=18242&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=9b4d65da1531e13c4a9e3f5a986b03e4&searchtype=a Qie and Dube, 2010] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Effect of CTA.jpg| thumb|center|300px|Effect of chain transfer agent and cross-linker concentration in making of PSAs]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | | | + | ====Effect of flexible substrates on PSAs performance==== |
| − | | | + | The fracture energy (fracture toughness) of tapes during globally elastic unpeeling is often calculated from the relation G=P/b(1−cos θ). A study suggested that this expression is correct for elastic peeling from rigid substrates but it gives misleading results when peeling from reversible flexible substrates. [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6TW7-46RKMVR-1&_user=10&_coverDate=12%2F31%2F2002&_alid=1598155857&_rdoc=14&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_origin=search&_zone=rslt_list_item&_cdi=5555&_sort=r&_st=13&_docanchor=&view=c&_ct=18242&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=5a2c01b1375cc8e2d6e2d69ed8cd8aa4&searchtype=a Steven-Fountain et al., 2002] |
| − | | | + | |
| − | | | + | ==PSA performance measurement== |
| + | |||
| + | PSAs polymeric materials effect tack, peel and shear strength . Inherent properties such as copolymer composition and microstructure, molecular weight and distribution are among the most influential factors affecting PSA properties directly as well as indirectly through their influence on physical properties (e.g., the glass transition temperature, Tg) and thus, rheological properties of the polymer (e.g., viscoelastic regions, moduli). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore, PSA is the result of a fine balance between these three major, interrelated properties. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Tack=== | ||
| + | It is a measure of the force required to remove, say a foam gasket and its adhesive, from the substrate. It usually refers to the initial attraction of the adhesive to the substrate. Tack can be measured by four basic methods these are loop tack, rolling ball, Quick stick and probe measurement devices. [http://www.adhesivestoolkit.com/Docu-Data/NPLDocuments/P%20A%20J/PAJ%20Reports/PAJ1%20Reports/PAJ1%20Report%205.pdf Review Of Methods For The Measurement Of Tack] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Peel strength=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Peel strength is measured as a force required to remove a standard PSA strip from a specified test surface under a standard test angle (e.g., 90° or 180°) under standard conditions. Much like tack, manufacturers control adhesion to create different products based on user requirements. After a PSA has been applied to the substrate, adhesion continues to increase for a period of time — typically 24 hr. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Shear strength=== | ||
| + | Shear strength is the internal or cohesive strength of the adhesive mass. Usually, it is determined as the length of time it takes for a standard strip of PSA to fall from a test panel after application of a load. Usually, tack and adhesion decrease as shear strength increases. [http://www.informaworld.com/smpp/section?content=a713642457&fulltext=713240928 Emulsion-Based Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives: A Review] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==PSA products== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The most common products that utilize PSAs are tapes, labels, and protective films. The PSA sector is among the fastest growing in the adhesive market, making the search for new pressure-sensitive products (PSP) and applications highly competitive. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''PSA tapes:''' Self-adhesive materials usually produced by coating an adhesive onto a carrier and used as a continuous web. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''PSA labels:''' Self-adhesive laminated carrier materials. The self-adhesive layer is protected with a supplemental material (release liner). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Protective films:''' Carrier material possesses built-in or built-on self-adhesive properties. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Recycling issues with PSA== | ||
| + | |||
| + | PSAs exact a considerable cost on the paper recycling industry, an estimated $700 million per year. Most paper recycling systems converts paper into pulp in presence of water, which is then transformed back into paper. PSAs do not dissolve in water, but rather fragment into smaller particles during the repulping process. These particles are known as stickies, get deformed under heat and pressure, making them difficult to screen or filter out of the pulp. Stickies can become lodged on papermaking and can cause damage to equipment or even in the paper. [http://www.calrecycle.ca.gov/ReduceWaste/Business/officepaper/PSAFacts.htm Source] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {|border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" align = "center" width="90%" | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''Sr. No.''' | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''"Sticky" PSA Product''' | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''Alternative Product/Procedure''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''1''' |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|Address Labels |
| − | | | + | |align = "left"|1. Print addresses directly on envelopes<br>2. Using glassine (cellulose) film window or filmless window envelopes, and print mailing addresses directly on the letter to show through the window.<br>3. Handprint addresses directly on large mailing envelopes.. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''2''' |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|Sticky Notes |
| − | + | |align = "left"|1.Use scratch paper for notes and secure with paper clips. | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''3''' |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|Postage Stamps |
| − | + | |align = "left"|1. Use moisture-activated postage stamps<br>2. Postal meter that prints postage directly on envelopes or that uses moisture-activated meter tape | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''4''' |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|File Folder Index Labels |
| − | + | |align = "left"|1. Handprint file subjects directly on index tabs, instead of using an index label. When recycling file folders with index labels, tear off the index tab. | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#B8CCE4"|'''5''' |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|Closure Tabs |
| − | + | |align = "left"|1. Sharply folding fliers and newsletters is often sufficient to send them safely and securely through the mail. | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| − | = | + | ==Search strategy== |
| − | + | Search strategy last updated on: 7th January 2011 | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | {|border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" align = "center" width="60%" | |
| − | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''Sr. No.''' | |
| − | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''Search string''' | |
| − | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''Hits''' | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#C5BE97" colspan = "3"|'''Google''' |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''1''' |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive making |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|7,510,000 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''2''' |
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive application |
| + | |align = "center"|7,650,000 | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''3''' |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive automobile |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|436,000 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''4''' |
| − | |align = "center" | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive automotive |
| + | |align = "center"|479,000 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''5''' |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive drug delivery |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|275,000 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''6''' |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive tack* |
| + | |align = "center"|354,000 | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''7''' |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive product |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|8,120,000 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''8''' |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive recycl* |
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|447,000 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#C5BE97" colspan = "3"|'''Google scholar''' |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''1''' |
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive making |
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|21,50,000 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''2''' |
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive application |
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|21,50,000 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#C5BE97" colspan = "3"|'''Scirus''' |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''1''' |
| − | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive making | |
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|130,055 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''2''' |
| − | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive application | |
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|200,950 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''3''' |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive product |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|136,169 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#C5BE97" colspan = "3"|'''Sciencedirect''' |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''1''' |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive electronics |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|2,450 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''2''' |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive making |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|7,212 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''3''' |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive application |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|15,405 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''4''' |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive automobile |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|951 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center"|''' | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''5''' |
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive automotive |
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|1,406 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''6''' |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive drug delivery |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|2,876 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#C5BE97" colspan = "3"|'''Springerlink''' |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''1''' |
| − | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive making | |
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|2,149 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''2''' |
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive application |
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"|3,901 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#C5BE97" colspan = "3"|'''Google images''' |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''1''' |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive making |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|3,580,000 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''2''' |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive application |
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"|2,210,000 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#95B3D7"|'''3''' |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|Pressure sensitive adhesive electronics |
| − | + | |align = "center"|1,690,000 | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | |} | |
| − | + | ||
| − | | | + | ==Market Information== |
| + | * According to a report from the Business Communications Company, the 2001 US market for specialty adhesives was about $5.7 billion, and is forecast to grow at 4.3% per year, with medical and dental applications being the fastest-growing sector at 5.9% per year. [http://www.marketfile.com/print/paint/title5/index.htm Source] | ||
| + | * Frost and Sullivan report the size of the European PSA market (medical and non-medical) to be $620 million in 2000, forecast to grow to $796 million in 2007. [http://www.engineeringtalk.com/news/fro/fro122.html Source] | ||
| + | * The world value of the overall adhesives market is estimated at US $22 billion. | ||
| + | * '''Total Market Expected to Grow at a CAGR of 9 Percent''': The U.S. PSA markets for labels and narrow-web graphics is expected to growth with a CAGR of 9 percent during the years 2006–2012. The total U.S. PSA markets for labels and narrow-web graphics unit shipments are expected to continue to growth at a CAGR of 6.6 percent due to high end-user growth. The UV technology is a new technology that have started to receive wide acceptance in the industry and that segment of the industry is a fragmented and developing segment with growth rates in double digits. While the solvent-based PSAs are expected to show decreasing growth percents, the water-based and solvent-based segments are expected to growth in the lines of the total industry. [http://www.frost.com/prod/servlet/report-brochure.pag?id=F652-01-00-00-00 Source] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * According to '''World Adhesives File 2000-2005''', the leading handful of adhesives suppliers, including pressure sensitive companies, already controlled almost half the global market in 1999. Henkel leads the way with an estimated 12% global market share, which will probably increase to around 14% with the purchase of Dexter’s adhesives interests. Pressure sensitive suppliers 3M and Avery Dennison are ranked second and third, with 9% and 7% shares respectively, followed jointly by National Starch and H.B. Fuller — both at 6%. The newly enlarged Atofina and Rohm and Haas follow closely behind.” [http://answers.google.com/answers/threadview?id=60487 Source] | ||
| + | * Growth of the world market averages about 2-3% per year. | ||
| + | * Packaging adhesives make up the majority of the market. | ||
| + | * The electronic and medical adhesives market is currently experiencing the most rapid growth. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Market leaders by country are as follows: | ||
| + | ** United States - approximately 2.6 tonnes annually | ||
| + | ** China | ||
| + | ** Japan | ||
| + | ** Germany | ||
| + | ** UK [[image:players_logo.jpg|right|500 px]] | ||
| + | * Market leaders by company(which account for one-third of the market share) are: | ||
| + | ** Henkel | ||
| + | ** 3M | ||
| + | ** Avery Denison | ||
| + | ** HB Fuller | ||
| + | ** National Starch | ||
| + | ** Atofina | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Intellectual Property== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Patent Search Table=== | ||
| + | {|border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" width="100%" | ||
| + | |colspan = "5"| | ||
| + | * Patent search on Micropat | ||
| + | * Databases searched: '''USG USA EPA EPB WO JP DEG DEA DET DEU GBA FRA''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |bgcolor = "#FFFF99"|'''Query.No.''' |
| − | | | + | |bgcolor = "#FFFF99"|'''Searched Sections''' |
| − | | | + | |bgcolor = "#FFFF99"|'''Years Searched''' |
| − | |bgcolor = "# | + | |bgcolor = "#FFFF99"|'''Query''' |
| − | |bgcolor = "# | + | |bgcolor = "#FFFF99"|'''Hits''' |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |1 |
| − | | | + | |Claims, Title or Abstract |
| − | + | |1836 – Date | |
| − | | | + | ||(rubber OR acryl* OR silicone OR oil*1 OR resin*1 OR ethylen* OR isoprene OR terpene OR copolymer* OR vinyl* OR siloxane* ((acid OR anhydride) ADJ1 (acrylic OR crotonic OR (vinyl ADJ1 acetic) OR fumaric OR maleic OR malonic OR succinic OR itaconic OR citraconic)) OR polymer* OR styrene OR ester*) SAME (((pressure ADJ1 sensitive) NEAR2 (adhesive* OR glue OR paste OR (binding ADJ1 agent) OR (epoxy ADJ1 resin*) OR film) OR PSA OR PSAs) OR (adhesion* WITH (peel OR tensile OR shear) OR stick*) OR (radical* ADJ1 (initiator* OR maker*))) |
| − | | | + | |76006 |
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |2 |
| − | | | + | |Claims, Title or Abstract |
| − | + | |1836 – Date | |
| − | | | + | |(((low ADJ surface ADJ energy) WITH (substrate*1 OR polymer OR compound* OR material OR film)) OR (surface ADJ1 tension) OR (surface ADJ1 rough*) OR viscosity OR (oily ADJ surface) OR (low ADJ1 energy ADJ1 surface*)) AND (polyolefin*1 OR polyethylene*1 OR polypropylene*1 OR (polyvinyl ADJ1 chloride ADJ1 film) OR (oil ADJ1 contaminated ADJ1 metal) OR polybutene OR polyisoprene*1 OR (polyvinylidene ADJ1 fluoride*) OR polytetrafluoroethylene*1 OR polyester*1 OR polyamide*1 OR polyacetal*1 OR polystyrene*1 OR polyurethane* OR polyurea OR silan* OR polycarbonate*) |
| − | | | + | |75602 |
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |3 |
| − | | | + | |Claims, Title or Abstract |
| − | + | |1836 – Date | |
| − | + | |1 AND 2 | |
| − | + | |2272 | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |} |
| − | + | * Total number of patents - 2272 | |
| − | |align = "center" | + | * Total number of unique patent families - 1483 |
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | ==<span style="color:#C41E3A">Like this report?</span>== | |
| − | + | <p align="center"> '''This is only a sample report with brief analysis''' <br> | |
| − | + | '''Dolcera can provide a comprehensive report customized to your needs'''</p> | |
| + | {|border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" align="center" " | ||
| + | |style="background:lightgrey" align = "center" colspan = "3"|'''[mailto:info@dolcera.com <span style="color:#0047AB">Buy the customized report from Dolcera</span>]''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center"| | + | | align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/services/ip-patent-analytics-services Patent Analytics Services] |
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/services/business-research-services Market Research Services] |
| − | + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/tools/patent-dashboard Purchase Patent Dashboard] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |align = "center"|[ | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/services/ip-patent-analytics-services/patent-search/patent-landscapes Patent Landscape Services] |
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/research-processes Dolcera Processes] |
| − | + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/industries Industry Focus] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |align = "center"|[ | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center | + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/services/ip-patent-analytics-services/patent-search/patent-landscapes Patent Search Services] |
| − | + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/services/ip-patent-analytics-services/alerts-and-updates Patent Alerting Services] | |
| − | + | |align = "center"| [http://www.dolcera.com/website_prod/tools Dolcera Tools] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |align = "center"| | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | <br> | ||
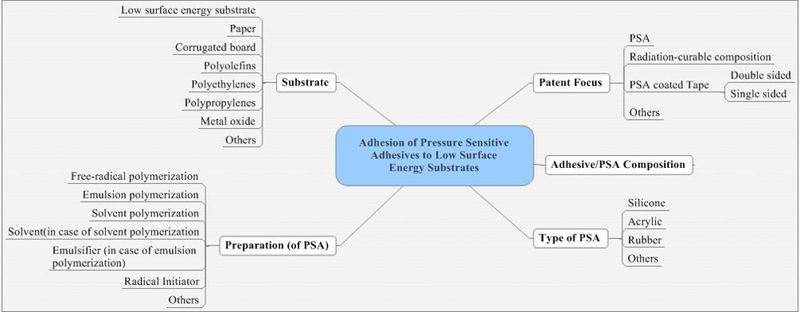
| − | = | + | ===Taxonomy for analysis=== |
| + | [[Image:adhesion-3Mnew2.jpg|thumb|center|800px|Taxonomy map - Adhesion]] | ||
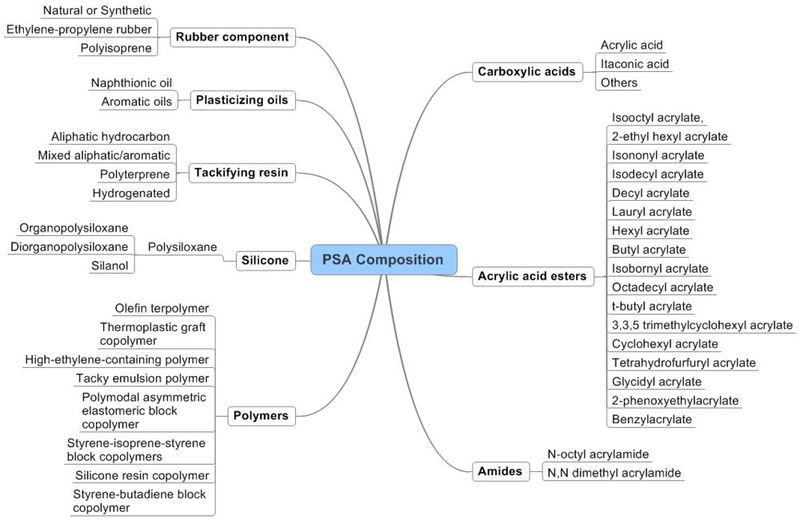
| − | == | + | ===Taxonomy for PSA composition=== |
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:adhesion-final version.jpg|thumb|center|800px|Taxonomy map - Adhesion]] |
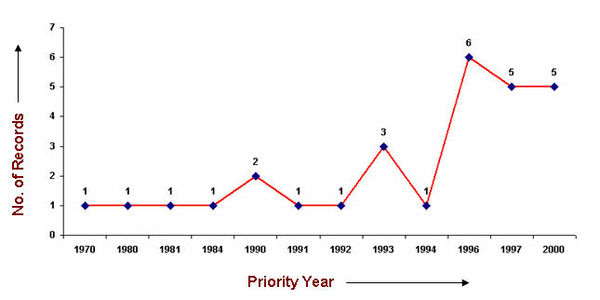
| − | [[ | + | ===IP Activity=== |
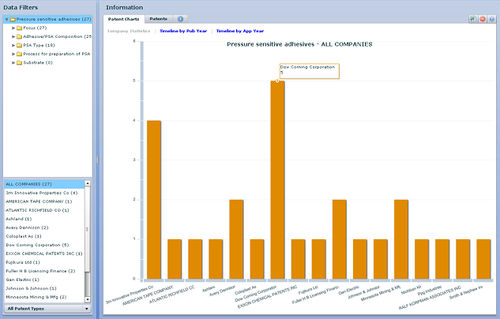
| + | [[image:Priority year_PSA.jpg|center|600 px|thunb|Competitors]] | ||
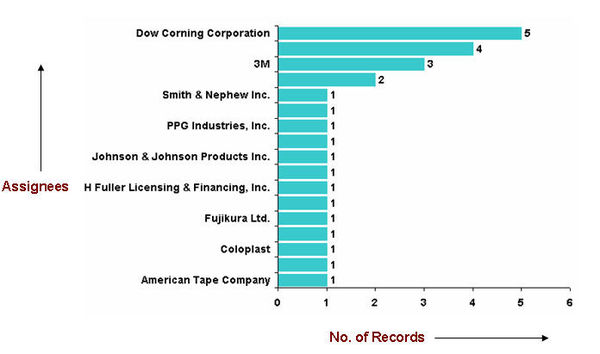
| − | = | + | ===Major Competitors=== |
| − | + | [[image:competitors_PSA.jpg|center|600 px|thunb|Competitors]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | == | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Composition components matrix=== | ||
{|border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" width="100%" | {|border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4" width="100%" | ||
| − | |bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#C0C0C0"|'''Assignees''' |
| − | |bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#C0C0C0"|'''Rubber''' |
| − | |bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#C0C0C0"|'''Silicone''' |
| − | |bgcolor = "# | + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#C0C0C0"|'''Polymers''' |
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#C0C0C0"|'''Acrylic''' | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#C0C0C0"|'''Tackifying resin''' | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#C0C0C0"|'''Plasticizer oil''' | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#C0C0C0"|'''Carboxylic acids''' | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#C0C0C0"|'''Acid Esters''' | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#C0C0C0"|'''Priority Year''' | ||
| + | |align = "center" bgcolor = "#C0C0C0"|'''Patent numbers''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" | + | |rowspan = "5"|3M Innovative Properties Company |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|x |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|x |
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |2000 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6630531 US6630531]</u></font> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|x |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|x |
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |2000 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6632872 US6632872]</u></font> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|x |
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |2000 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6455634 US6455634]</u></font> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|x |
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |1993 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5612136 US5612136]</u></font> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" | + | |align = "center"| |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| − | + | |align = "center"|x | |
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |1993 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5602221 US5602221]</u></font> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |align = "center" | + | |American Tape Company |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|x |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| − | + | |align = "center"| | |
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |1997 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5798175 US5798175]</u></font> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Ashland Oil, Inc. |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|x |
| − | + | |align = "center"| | |
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |1991 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5434213 US5434213]</u></font> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |rowspan = "4"|Atlantic Richfield Company |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |1984 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4656213 US4656213]</u></font> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |1996 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5817426 US5817426]</u></font> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |1996 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5817426 US5817426]</u></font> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |1997 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6461707 US6461707]</u></font> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Coloplast | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |1980 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6437038 US6437038]</u></font> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |rowspan = "5"|Dow Corning Corporation | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |1970 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5916981 US5916981]</u></font> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |1990 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6337086 US6337086]</u></font> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| − | == | + | | |
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |1990 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6121368 US6121368]</u></font> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| − | + | |align = "center"| | |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|x |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|x |
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |1994 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5561203 US5561203]</u></font> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |1996 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5861472 US5861472]</u></font> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Exxon Chemical Patents Inc. |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |1993 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5714254 US5714254]</u></font> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Fujikura Ltd. |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |2000 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6388556 US6388556]</u></font> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |General Electric Company |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |2000 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6387487 US6387487]</u></font> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |H Fuller Licensing & Financing, Inc. |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|x |
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |1996 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5741840 US5741840]</u></font> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |H. B. Fuller Licensing & Financing, Inc. |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|x |
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |1997 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5869562 US5869562]</u></font> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Johnson & Johnson Products Inc. | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |1981 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4335026 US4335026]</u></font> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | |Nichiban Company Limited | |
| − | + | |align = "center"|x | |
| − | + | |align = "center"| | |
| − | + | |align = "center"| | |
| − | + | |align = "center"| | |
| − | + | |align = "center"| | |
| − | + | |align = "center"| | |
| − | + | |align = "center"| | |
| − | + | |align = "center"| | |
| − | | | + | |1997 |
| − | | | + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6274235 US6274235]</u></font> |
| − | | | + | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | | | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |None |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|x |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|x |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|x |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|x |
| − | | | + | |1996 |
| − | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[ | + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://appft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PG01&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=%2220030136510%22.PGNR.&OS=DN/20030136510&RS=DN/20030136510 US20030136510]</u></font> |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |PPG Industries, Inc. |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|x |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|x |
| − | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http:// | + | |align = "center"|x |
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"|x | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |1996 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5776548 US5776548]</u></font> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Ralf Korpman Associates, Inc. |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"|x |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| − | | | + | |align = "center"| |
| − | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http:// | + | |align = "center"| |
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |align = "center"| | ||
| + | |1992 | ||
| + | |<font color="#0000FF"><u>[http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5760135 US5760135]</u></font> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | ===Technology Tree=== | ||
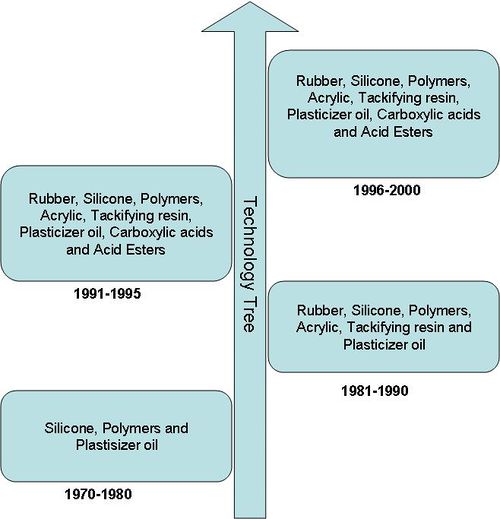
| − | [[image: | + | As it is evident from the the technology tree below, although the IP activity in the area of Pressure sensitive adhesive was initiated during 1970s, companies are continuously trying new combinations of different components. |
| + | [[image:Technology tree.jpg|center|500 px]] | ||
| − | =<span style="color:#C41E3A">Like this report?</span>= | + | ==Key findings== |
| + | * In the medical field, pressure-sensitive adhesive tapes are used for many different applications in the hospital and health areas and also they can be used to adhere two surfaces together such as the flaps of packing material or fabric to a surface | ||
| + | * In many commercial applications of pressure-sensitive adhesives, it would be preferred to use an acrylate polymer or copolymer having an intrinsic viscosity of at least about 2.5 dl/g | ||
| + | * Ideally, a process for producing an acrylate-based polymer for a pressure-sensitive adhesive provides a means for controlling both molecular weight, i.e., intrinsic viscosity, and molecular weight distribution. | ||
| + | * Pressure-sensitive adhesives require a delicate balance of viscous and elastic properties that result in a four-fold balance of adhesion, cohesion, stretchiness and elasticity. Pressure-sensitive adhesives generally comprise elastomers that are either inherently tacky, or elastomers or thermoplastic elastomers that are tackified with the addition of tackifying resins. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Analysis Sheet== | ||
| + | [[Media:Sample analysis sheet.xls|Sample Analysis Sheet]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==<span style="color:#C41E3A">Like this report?</span>== | ||
<p align="center"> '''This is only a sample report with brief analysis''' <br> | <p align="center"> '''This is only a sample report with brief analysis''' <br> | ||
'''Dolcera can provide a comprehensive report customized to your needs'''</p> | '''Dolcera can provide a comprehensive report customized to your needs'''</p> | ||
| Line 794: | Line 879: | ||
|} | |} | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| + | ==Contact Dolcera== | ||
| − | + | {| style="border:1px solid #AAA; background:#E9E9E9" align="center" | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | =[ | + | ! style="background:lightgrey" | Contact Dolcera |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Email''': [mailto:info@dolcera.com info@dolcera.com] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Phone''': +1-650-269-7952 | ||
| + | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 05:43, 27 July 2015
Contents
- 1 Dashboard
- 2 Overview
- 3 Application of PSA
- 4 Making of PSAs
- 4.1 Effect of important parameters on PSA making and performance
- 4.1.1 Effect of polymer molecular weight and crosslinking reactions on the end-use properties of PSAs
- 4.1.2 Effect of composition on Mechanical behaviours and fracture energy of PSAs
- 4.1.3 Effect of tackifier on PSAs
- 4.1.4 Effect of chain transfer agent and cross-linker concentration in making of PSAs
- 4.1.5 Effect of flexible substrates on PSAs performance
- 4.1 Effect of important parameters on PSA making and performance
- 5 PSA performance measurement
- 6 PSA products
- 7 Recycling issues with PSA
- 8 Search strategy
- 9 Market Information
- 10 Intellectual Property
- 11 Like this report?
- 12 Key findings
- 13 Analysis Sheet
- 14 Like this report?
- 15 Contact Dolcera
Dashboard
Dolcera dashboard provides quick and easy navigation through the technology segments. Below is the snapshot of how it look like. Click on the link Dolcera Dashboard for Pressure Sensitive Adhesives.
Overview
Pressure sensitive adhesive (PSA, self adhesive, self stick adhesive) is adhesive that forms a bond when pressure is applied to marry the adhesive with the adherend. No solvent, water, or heat is needed to activate the adhesive. It is used in pressure sensitive tapes, labels, note pads, automobile trim, and a wide variety of other products.
As the name "pressure sensitive" indicates, the degree of bond is influenced by the amount of pressure which is used to apply the adhesive to the surface.
Surface factors such as smoothness, surface energy, removal of contaminants, etc. are also important to proper bonding.
PSAs are usually designed to form a bond and hold properly at room temperatures. PSAs typically reduce or lose their tack at cold temperatures and reduce their shear holding ability at high temperatures: Specialty adhesives are made to function at high or low temperatures. It is important to choose an adhesive formulation which is designed for its intended use conditions.
Surface Energy
- Surface energy is a measure of how well an adhesive wets out over the surface of the material to which it is applied.
- The most common method of determining the surface energy is to measure the contact angle of a water droplet on the substrate surface.
- The contact angle between the solid and the fluid is the angle measured within the fluid, between the solid surface and the tangent plane to the liquid surface at the point of intersection.
- A contact angle of greater than 90° indicates that the fluid (which is ink or adhesive in this case) has not wet the surface. Conversely an angle of less than 90° means that the fluid has wet the surface - if the angle approaches zero then the surface is completely wetted by the fluid.
- The surface energy or the wetability of a particular substrate is measured in dynes/cm. Source
Low Surface Energy Substrates
- Low energy plastics, such as polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE) and Teflon (PTFE) are essentially "non- stick" plastics.
- Their molecular structure inhibits the adhesion and printing processes - this molecular structure is basically inert or inactive – these polymers are said to have a low surface energy.
- Materials with low surface energy (LSE) do not allow adhesives to wet out, while materials with high surface energy (HSE) provide excellent wet-out, providing the best adhesion.
- Rubber-based adhesives usually provide better adhesion to LSE surfaces.
- Some substrates require special treatment such as corona treating, primers, top coating, etc., in order to achieve better adhesion.
- On some LSE substrates, adhesion levels improve the longer adhesive is applied. Source
Adhesion
- Adhesion is the molecular force of attraction between unlike materials.
- Adhesion and cohesion, attractive forces between material bodies. A distinction is usually made between an adhesive force, which acts to hold two separate bodies together (or to stick one body to another) and a cohesive force, which acts to hold together the like or unlike atoms, ions, or molecules of a single body.
- For example water molecules stick to each other. This is caused by hydrogen bonds that form between the slightly positive and negative ends of neighboring molecules.
- Water is found in drops; perfect spheres. It’s hard to imagine water behaving any other way due to cohesion and water molecules stick to other surfaces due to adhesion.Source
Application of PSA
Application in electronics and electrical industry
Electrical grade PSAs are critical components in the design many of today's electrical and electronic components in the electrical industry. The construction of this type of PSA is difficult since lower concentration of conductive filler must be used in order to prevent the drying out of polymer by the conductive filler, with attendant loss of tack. The conductivity of electrically conductive PSA in the direction of pressure action is to a certain extend depend on the direction of pressure applied Florian, 2003
Electrical grade PSAs are designed and manufactured using materials using material that are physically and chemically stable in the presence of humidity and electrical stress. The acrylic high tack PSAs works very well in static and dynamic joints. The PSA agents are used in three forms i.e. modified aqueous dispersions or solutions in different solvents and as hot melts adhesives. PSA tapes find application in electronic assemblies Reliability of Pressure-Sensitive Adhesive Tapes for Heat Sink Attachment in Air-Cooled Electronic Assemblies
Application in automobile industry
While mechanical fasteners will always be the choice when maximum torque and linear force are required in automobile industry, pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSAs) can often provide a better method of joining or bonding than traditional screws, nuts, bolts, rivets and welds.
The design, performance, and production reasons for replacing mechanical or fusion fastening methods with PSAs include, but are not limited to:
- Distributing stress over the entire bonded area: The concentrated stress of mechanical fasteners can be eliminated and design engineers can specify lighter, thinner materials without sacrificing durability and product integrity.
- Bonding dissimilar materials: The ability to bond two totally different substrates can yield a superior combination for product strength and performance. PSAs are an ideal counterbalance for varying factors of expansion between surfaces, such as laminating layers of metal.
- Maintaining assembled substrate integrity: Less machining and finishing means more latitude for design engineers and improved aesthetics for greater consumer appeal.
- Incorporating fatigue resistance: PSAs bring great flexibility, allowing for high extension and recovery under heavy loads.
- Durability by design: PSAs fill voids and gaps and can bond loose-fitting parts.
Increasing production efficiency: PSAs reduce material requirements, provide product weight reduction, require fewer assembly and finishing steps, and minimize training FLEXcon white paper
Medical applications
There are two essential requirements of medical PSAs, that they should stick firmly to a difficult substrate (skin) and that they should be easily and cleanly removed from that substrate when desired. These requirements would seem to be in conflict: a high peel force usually signals the ability to stick firmly, while a low force is needed when removing dressings by peeling.
A number of ways have been considered to resolve this conflict. These may be divided into two broad categories: those that make the best of existing PSA technology, broadly taking a physical approach, and those that introduce novel chemistry into the process. Physical approaches consider such details as the dependence of peel force on peel angle, peel rate, backing materials, the deformation of the skin during peeling and use of barrier films and solvents. As an alternative to simply making the best of the physics of the peeling process, various workers have devised chemical systems for making the adhesive less strongly adhering at the time of removal. These systems usually consist of introducing a ‘switch’ mechanism into a strongly adhering adhesive so that its adherence may be reduced significantly at the time of removal by operation of the ‘switch’. Means of activating the ‘switch’ include: heat (warming or cooling), application of water via an absorbent backing and exposure to visible light. These may produce physical or chemical changes in the adhesive Chivers, 2001
PSAs drive transdermal delivery
Transdermal or through-the-skin delivery of drugs has assumed an important place in drug therapy, eliminating many of the shortcomings of syringes and pills. Active Transdermal Delivery Systems The three most commonly used adhesives used for transdermal delivery are polyisobutylenes, polyacrylates and silicones Tan and Pfister, 1999
- In a typical disk drive, PSAs are applied to the base casting to secure the motor-mounting flange and motor assembly
Application in aerospace industry
Aerospace manufacturers uses PSAs to assemble sheet-metal components into sub assemblies. The aerospace industry, primarily satellite manufacturers, have expressed the need for a low outgas, thermally stable, adhesive tape which can work at both high, 175ºC, and low, -100ºC, temperatures. New silicone PSA was fabricated to pass, low outgassing requirements of 1% or less Total Mass Loss (TML) and 0.1% or less Collectable Volatile Condensable Materials (CVCM) Riegler, 2005.
Making of PSAs
Although PSPs can be obtained by different polymerization processes (i.e., emulsion, solution, hot-melt, or radiation curing), much attention has recently been devoted to the utilization of more environmentally friendly processes such as emulsion polymerization. Soft polymer networks are commonly used as previous termpressure sensitive adhesivesnext term (PSAs). This is due to their unique ability to deform and yet to resist flow. These contradictory requirements indicate that the mechanical properties are finely tuned, and that the types of deformation upon application are carefully considered. Variety of PSAs can be prepared by mixing a linear vinyl terminated polymer with a silane terminated f-functional cross-linker. Jensen et al., 2009
| Sr. No. | PSA process | Chemical composition | Time of launch |
| 1 | Solvent-based | Rubber/resin, acrylics, silicones | Since 19th century |
| 2 | Hot-melt | Block copolymers, acrylics | 1940s |
| 3 | Emulsion (water)-based | Acrylics, natural and synthetic rubber, ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer | 1970s |
| 4 | Radiation-cured | Acrylics, rubber | 1970s |
| Sr. No. | Properties | Solvent-based: acrylic | Hot-melt: styrene-isobutylene-styrene. | Emulsion based: acrylics |
| 1 | PS performance | Excellent | Excellent | Very good |
| 2 | Ease of compounding | Moderate | Difficult | Easy |
| 3 | Formulation flexibility | Limited | Excellent | Moderate |
| 4 | Coating method flexibility | Limited | Poor | Excellent |
| 5 | Ease of changeover | Limited | Poor | Excellent |
| 6 | PSA reproducibility | Excellent | Limited | Excellent |
| 7 | Aging properties | Excellent | Poor | Excellent |
| 8 | Clarity/color | Excellent | Poor | Excellent |
| 9 | Safety/toxicity | Poor | Poor | Excellent |
| 10 | Raw material costs | High | Low | Medium |
| 11 | Coating/compounding costs | High | Medium | Low |
Effect of important parameters on PSA making and performance
Effect of polymer molecular weight and crosslinking reactions on the end-use properties of PSAs
In a study wherein polymer molecular weight and polymer microstructure were regulated using different chain transfer agent (CTA) concentrations and by addition of a diacrylic monomer (MM) it was shown that all of the measured adhesion properties strongly depend on molecular weight of the synthesized polymer and on the amount of gel phase Kajtna et al., 2009
Effect of composition on Mechanical behaviours and fracture energy of PSAs
In a study it was shown that the mechanical behaviour depend on their composition but majority of fracture energy is dissipated on the first millimetre near the bending zone where fibrils elongation is maximum. Observations of interfaces between PSAs and glass substrate underline that fracture energy varies linearly according to the contact area Horgnies et al., 2007
Effect of tackifier on PSAs
To study the effect of tackifier (such as hydrogenated cyclo-aliphatic resin) a model system consisting of polystyrene-b-polyisoprene-b-polystyrene triblock copolymer was prepared. Tackifier increased the peel adhesion significantly and the increase became stronger above 40 wt% tackifier. The higher peel adhesion was obtained in the system with the larger amount of agglomerates of tackifier in the polyisoprene matrix. Sasaki et al., 2008
Effect of chain transfer agent and cross-linker concentration in making of PSAs
In a study it was shown that a constant cross-linker concentration, one can manipulate the polymer micro-structure by adding varying amounts of chain transfer agent. Three examples of these micro-structures are depicted below which show a tight gel network with long-chain sol polymers, a loose gel network with shorter sol polymers, and an imperfect gel structure with highly branched sol polymers. By manipulating the micro-structure, previous termpressure-sensitive adhesivenext term performance can be affected. Qie and Dube, 2010
Effect of flexible substrates on PSAs performance
The fracture energy (fracture toughness) of tapes during globally elastic unpeeling is often calculated from the relation G=P/b(1−cos θ). A study suggested that this expression is correct for elastic peeling from rigid substrates but it gives misleading results when peeling from reversible flexible substrates. Steven-Fountain et al., 2002
PSA performance measurement
PSAs polymeric materials effect tack, peel and shear strength . Inherent properties such as copolymer composition and microstructure, molecular weight and distribution are among the most influential factors affecting PSA properties directly as well as indirectly through their influence on physical properties (e.g., the glass transition temperature, Tg) and thus, rheological properties of the polymer (e.g., viscoelastic regions, moduli).
Therefore, PSA is the result of a fine balance between these three major, interrelated properties.
Tack
It is a measure of the force required to remove, say a foam gasket and its adhesive, from the substrate. It usually refers to the initial attraction of the adhesive to the substrate. Tack can be measured by four basic methods these are loop tack, rolling ball, Quick stick and probe measurement devices. Review Of Methods For The Measurement Of Tack
Peel strength
Peel strength is measured as a force required to remove a standard PSA strip from a specified test surface under a standard test angle (e.g., 90° or 180°) under standard conditions. Much like tack, manufacturers control adhesion to create different products based on user requirements. After a PSA has been applied to the substrate, adhesion continues to increase for a period of time — typically 24 hr.
Shear strength
Shear strength is the internal or cohesive strength of the adhesive mass. Usually, it is determined as the length of time it takes for a standard strip of PSA to fall from a test panel after application of a load. Usually, tack and adhesion decrease as shear strength increases. Emulsion-Based Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives: A Review
PSA products
The most common products that utilize PSAs are tapes, labels, and protective films. The PSA sector is among the fastest growing in the adhesive market, making the search for new pressure-sensitive products (PSP) and applications highly competitive.
- PSA tapes: Self-adhesive materials usually produced by coating an adhesive onto a carrier and used as a continuous web.
- PSA labels: Self-adhesive laminated carrier materials. The self-adhesive layer is protected with a supplemental material (release liner).
- Protective films: Carrier material possesses built-in or built-on self-adhesive properties.
Recycling issues with PSA
PSAs exact a considerable cost on the paper recycling industry, an estimated $700 million per year. Most paper recycling systems converts paper into pulp in presence of water, which is then transformed back into paper. PSAs do not dissolve in water, but rather fragment into smaller particles during the repulping process. These particles are known as stickies, get deformed under heat and pressure, making them difficult to screen or filter out of the pulp. Stickies can become lodged on papermaking and can cause damage to equipment or even in the paper. Source
| Sr. No. | "Sticky" PSA Product | Alternative Product/Procedure |
| 1 | Address Labels | 1. Print addresses directly on envelopes 2. Using glassine (cellulose) film window or filmless window envelopes, and print mailing addresses directly on the letter to show through the window. 3. Handprint addresses directly on large mailing envelopes.. |
| 2 | Sticky Notes | 1.Use scratch paper for notes and secure with paper clips. |
| 3 | Postage Stamps | 1. Use moisture-activated postage stamps 2. Postal meter that prints postage directly on envelopes or that uses moisture-activated meter tape |
| 4 | File Folder Index Labels | 1. Handprint file subjects directly on index tabs, instead of using an index label. When recycling file folders with index labels, tear off the index tab. |
| 5 | Closure Tabs | 1. Sharply folding fliers and newsletters is often sufficient to send them safely and securely through the mail. |
Search strategy
Search strategy last updated on: 7th January 2011
| Sr. No. | Search string | Hits |
| 1 | Pressure sensitive adhesive making | 7,510,000 |
| 2 | Pressure sensitive adhesive application | 7,650,000 |
| 3 | Pressure sensitive adhesive automobile | 436,000 |
| 4 | Pressure sensitive adhesive automotive | 479,000 |
| 5 | Pressure sensitive adhesive drug delivery | 275,000 |
| 6 | Pressure sensitive adhesive tack* | 354,000 |
| 7 | Pressure sensitive adhesive product | 8,120,000 |
| 8 | Pressure sensitive adhesive recycl* | 447,000 |
| Google scholar | ||
| 1 | Pressure sensitive adhesive making | 21,50,000 |
| 2 | Pressure sensitive adhesive application | 21,50,000 |
| Scirus | ||
| 1 | Pressure sensitive adhesive making | 130,055 |
| 2 | Pressure sensitive adhesive application | 200,950 |
| 3 | Pressure sensitive adhesive product | 136,169 |
| Sciencedirect | ||
| 1 | Pressure sensitive adhesive electronics | 2,450 |
| 2 | Pressure sensitive adhesive making | 7,212 |
| 3 | Pressure sensitive adhesive application | 15,405 |
| 4 | Pressure sensitive adhesive automobile | 951 |
| 5 | Pressure sensitive adhesive automotive | 1,406 |
| 6 | Pressure sensitive adhesive drug delivery | 2,876 |
| Springerlink | ||
| 1 | Pressure sensitive adhesive making | 2,149 |
| 2 | Pressure sensitive adhesive application | 3,901 |
| Google images | ||
| 1 | Pressure sensitive adhesive making | 3,580,000 |
| 2 | Pressure sensitive adhesive application | 2,210,000 |
| 3 | Pressure sensitive adhesive electronics | 1,690,000 |
Market Information
- According to a report from the Business Communications Company, the 2001 US market for specialty adhesives was about $5.7 billion, and is forecast to grow at 4.3% per year, with medical and dental applications being the fastest-growing sector at 5.9% per year. Source
- Frost and Sullivan report the size of the European PSA market (medical and non-medical) to be $620 million in 2000, forecast to grow to $796 million in 2007. Source
- The world value of the overall adhesives market is estimated at US $22 billion.
- Total Market Expected to Grow at a CAGR of 9 Percent: The U.S. PSA markets for labels and narrow-web graphics is expected to growth with a CAGR of 9 percent during the years 2006–2012. The total U.S. PSA markets for labels and narrow-web graphics unit shipments are expected to continue to growth at a CAGR of 6.6 percent due to high end-user growth. The UV technology is a new technology that have started to receive wide acceptance in the industry and that segment of the industry is a fragmented and developing segment with growth rates in double digits. While the solvent-based PSAs are expected to show decreasing growth percents, the water-based and solvent-based segments are expected to growth in the lines of the total industry. Source
- According to World Adhesives File 2000-2005, the leading handful of adhesives suppliers, including pressure sensitive companies, already controlled almost half the global market in 1999. Henkel leads the way with an estimated 12% global market share, which will probably increase to around 14% with the purchase of Dexter’s adhesives interests. Pressure sensitive suppliers 3M and Avery Dennison are ranked second and third, with 9% and 7% shares respectively, followed jointly by National Starch and H.B. Fuller — both at 6%. The newly enlarged Atofina and Rohm and Haas follow closely behind.” Source
- Growth of the world market averages about 2-3% per year.
- Packaging adhesives make up the majority of the market.
- The electronic and medical adhesives market is currently experiencing the most rapid growth.
- Market leaders by country are as follows:
- United States - approximately 2.6 tonnes annually
- China
- Japan
- Germany
- UK
- Market leaders by company(which account for one-third of the market share) are:
- Henkel
- 3M
- Avery Denison
- HB Fuller
- National Starch
- Atofina
Intellectual Property
Patent Search Table
| ||||
| Query.No. | Searched Sections | Years Searched | Query | Hits |
| 1 | Claims, Title or Abstract | 1836 – Date | (rubber OR acryl* OR silicone OR oil*1 OR resin*1 OR ethylen* OR isoprene OR terpene OR copolymer* OR vinyl* OR siloxane* ((acid OR anhydride) ADJ1 (acrylic OR crotonic OR (vinyl ADJ1 acetic) OR fumaric OR maleic OR malonic OR succinic OR itaconic OR citraconic)) OR polymer* OR styrene OR ester*) SAME (((pressure ADJ1 sensitive) NEAR2 (adhesive* OR glue OR paste OR (binding ADJ1 agent) OR (epoxy ADJ1 resin*) OR film) OR PSA OR PSAs) OR (adhesion* WITH (peel OR tensile OR shear) OR stick*) OR (radical* ADJ1 (initiator* OR maker*))) | 76006 |
| 2 | Claims, Title or Abstract | 1836 – Date | (((low ADJ surface ADJ energy) WITH (substrate*1 OR polymer OR compound* OR material OR film)) OR (surface ADJ1 tension) OR (surface ADJ1 rough*) OR viscosity OR (oily ADJ surface) OR (low ADJ1 energy ADJ1 surface*)) AND (polyolefin*1 OR polyethylene*1 OR polypropylene*1 OR (polyvinyl ADJ1 chloride ADJ1 film) OR (oil ADJ1 contaminated ADJ1 metal) OR polybutene OR polyisoprene*1 OR (polyvinylidene ADJ1 fluoride*) OR polytetrafluoroethylene*1 OR polyester*1 OR polyamide*1 OR polyacetal*1 OR polystyrene*1 OR polyurethane* OR polyurea OR silan* OR polycarbonate*) | 75602 |
| 3 | Claims, Title or Abstract | 1836 – Date | 1 AND 2 | 2272 |
- Total number of patents - 2272
- Total number of unique patent families - 1483
Like this report?
This is only a sample report with brief analysis
Dolcera can provide a comprehensive report customized to your needs
Taxonomy for analysis
Taxonomy for PSA composition
IP Activity
Major Competitors
Composition components matrix
| Assignees | Rubber | Silicone | Polymers | Acrylic | Tackifying resin | Plasticizer oil | Carboxylic acids | Acid Esters | Priority Year | Patent numbers |
| 3M Innovative Properties Company | x | x | x | x | x | 2000 | US6630531 | |||
| x | x | x | x | 2000 | US6632872 | |||||
| x | x | 2000 | US6455634 | |||||||
| x | x | x | 1993 | US5612136 | ||||||
| x | x | x | 1993 | US5602221 | ||||||
| American Tape Company | x | x | 1997 | US5798175 | ||||||
| Ashland Oil, Inc. | x | x | x | 1991 | US5434213 | |||||
| Atlantic Richfield Company | x | x | x | x | 1984 | US4656213 | ||||
| x | x | x | x | 1996 | US5817426 | |||||
| x | x | x | 1996 | US5817426 | ||||||
| x | x | 1997 | US6461707 | |||||||
| Coloplast | x | x | x | 1980 | US6437038 | |||||
| Dow Corning Corporation | x | x | x | 1970 | US5916981 | |||||
| x | x | 1990 | US6337086 | |||||||
| x | 1990 | US6121368 | ||||||||
| x | x | 1994 | US5561203 | |||||||
| x | x | 1996 | US5861472 | |||||||
| Exxon Chemical Patents Inc. | x | x | 1993 | US5714254 | ||||||
| Fujikura Ltd. | 2000 | US6388556 | ||||||||
| General Electric Company | x | x | 2000 | US6387487 | ||||||
| H Fuller Licensing & Financing, Inc. | x | x | x | x | x | 1996 | US5741840 | |||
| H. B. Fuller Licensing & Financing, Inc. | x | x | x | 1997 | US5869562 | |||||
| Johnson & Johnson Products Inc. | x | x | x | x | 1981 | US4335026 | ||||
| Nichiban Company Limited | x | 1997 | US6274235 | |||||||
| None | x | x | x | x | 1996 | US20030136510 | ||||
| PPG Industries, Inc. | x | x | x | x | 1996 | US5776548 | ||||
| Ralf Korpman Associates, Inc. | x | 1992 | US5760135 |
Technology Tree
As it is evident from the the technology tree below, although the IP activity in the area of Pressure sensitive adhesive was initiated during 1970s, companies are continuously trying new combinations of different components.
Key findings
- In the medical field, pressure-sensitive adhesive tapes are used for many different applications in the hospital and health areas and also they can be used to adhere two surfaces together such as the flaps of packing material or fabric to a surface
- In many commercial applications of pressure-sensitive adhesives, it would be preferred to use an acrylate polymer or copolymer having an intrinsic viscosity of at least about 2.5 dl/g
- Ideally, a process for producing an acrylate-based polymer for a pressure-sensitive adhesive provides a means for controlling both molecular weight, i.e., intrinsic viscosity, and molecular weight distribution.
- Pressure-sensitive adhesives require a delicate balance of viscous and elastic properties that result in a four-fold balance of adhesion, cohesion, stretchiness and elasticity. Pressure-sensitive adhesives generally comprise elastomers that are either inherently tacky, or elastomers or thermoplastic elastomers that are tackified with the addition of tackifying resins.
Analysis Sheet
Like this report?
This is only a sample report with brief analysis
Dolcera can provide a comprehensive report customized to your needs
Contact Dolcera
| Contact Dolcera |
|---|
| Email: info@dolcera.com |
| Phone: +1-650-269-7952 |